Bio-remediation: A Natural Approach to Pollution Control by dr arshad alkhafaji
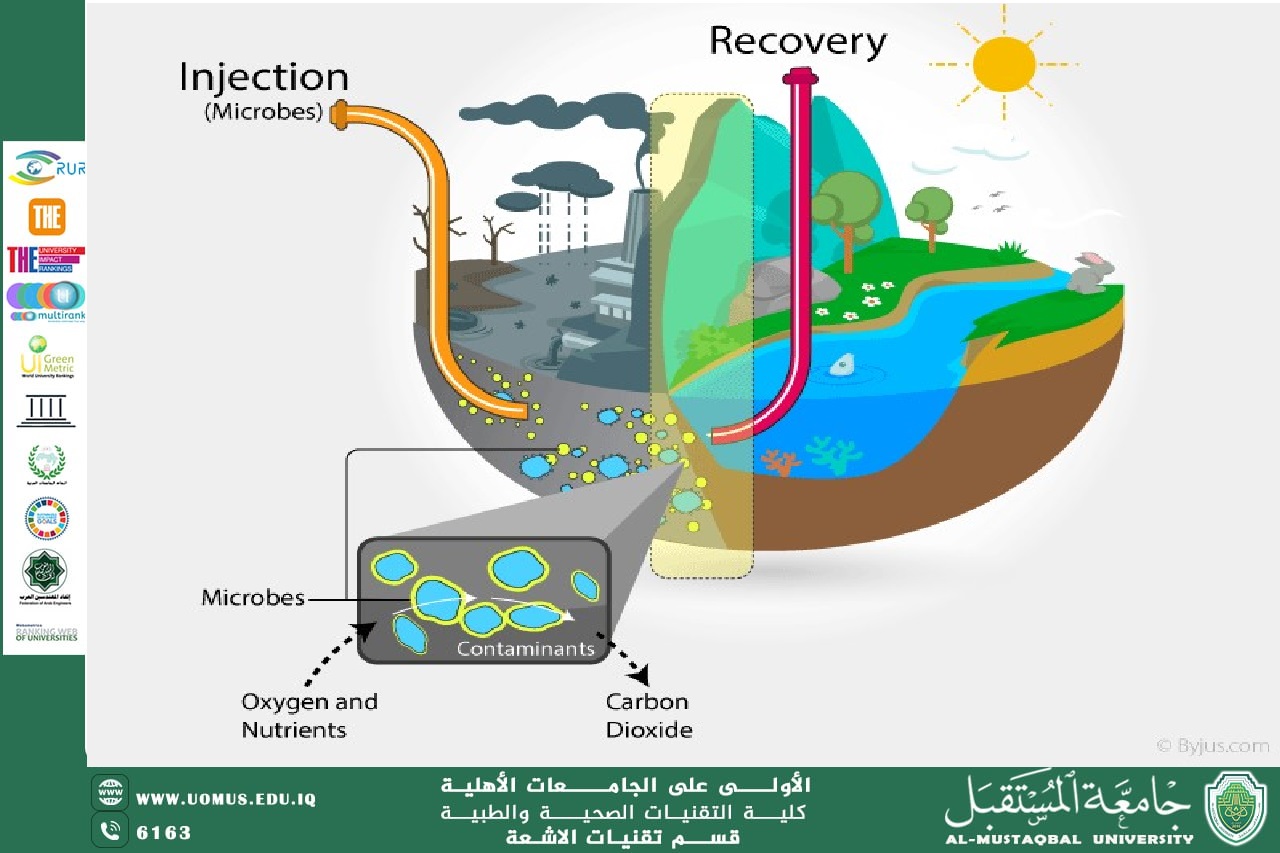
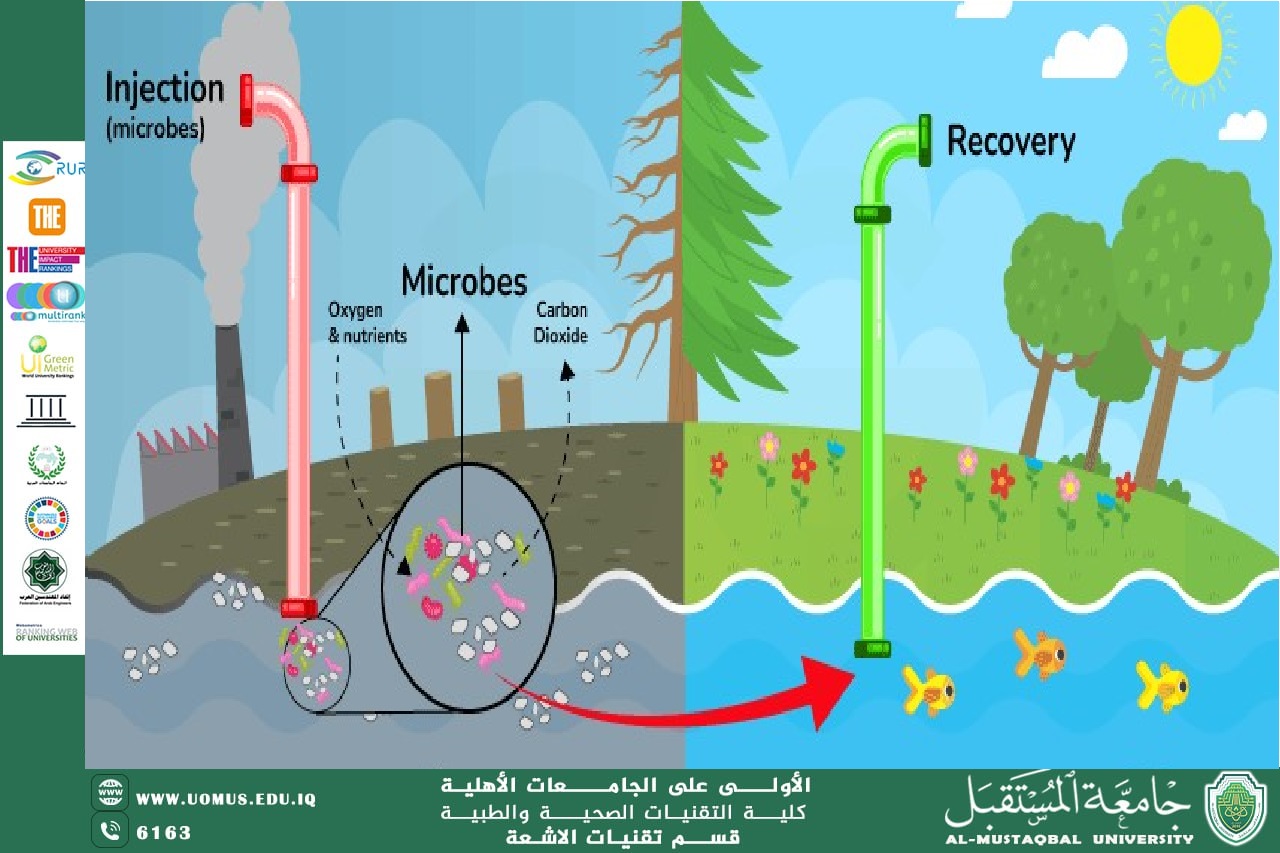
Bio-remediation: A Natural Approach to Pollution Control<br />Bioremediation is the process of using microorganisms, plants, or fungi to remove or neutralize contaminants from the environment. This eco-friendly technique is widely used to clean up oil spills, heavy metals, and industrial waste. Unlike traditional chemical methods, bioremediation relies on biological agents to break down pollutants into less harmful substances.<br />Types of Bio-remediation<br />1. Microbial Bioremediation<br />o Bacteria and fungi break down harmful chemicals in soil and water.<br />o Common organisms used include Pseudomonas and Bacillus species.<br />2. Phytoremediation<br />o Plants absorb toxins through their roots and store or break them down.<br />o Sunflowers and poplar trees are often used to clean up heavy metals.<br />3. Mycoremediation<br />o Fungi, such as Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster mushrooms), degrade organic pollutants.<br />o Effective for decomposing hydrocarbons and dyes.<br />Applications of Bioremediation<br />• Oil Spill Cleanup: Bacteria such as Alcanivorax degrade oil components in marine environments.<br />• Heavy Metal Removal: Certain plants absorb lead, arsenic, and mercury from contaminated soil.<br />• Industrial Waste Treatment: Microbes help break down toxic chemicals in wastewater.<br />• Land Reclamation: Bio-remediation restores polluted land for agricultural use.<br />Advantages of Bio-remediation<br />• Eco-Friendly: Uses natural organisms instead of harsh chemicals.<br />• Cost-Effective: Reduces expenses compared to traditional cleanup methods.<br />• Minimal Disruption: Works in situ without the need for excavation.<br />Challenges in Bio-remediation<br />• Slow Process: Can take months or years to fully clean a site.<br />• Specific Conditions Required: Microorganisms need optimal temperature, pH, and oxygen levels.<br />• Not Effective for All Pollutants: Some toxic substances resist biological breakdown.<br />Future of Bio-remediation<br />Advancements in genetic engineering and nanotechnology are improving bio-remediation efficiency. Scientists are developing genetically modified bacteria to target specific pollutants. With continued research, bio-remediation can become a primary tool for environmental restoration.<br />Conclusion<br />Bioremediation is a sustainable solution for pollution control. By harnessing the power of nature, we can clean up contaminated environments efficiently and safely. As technology evolves, bio-remediation will play an even greater role in environmental conservation.<br />