A scientific article by Professor Dr. Nasser Abdul-Hassan Nasser, titled:Digital Risks and Their Relation to Sustainability Goals
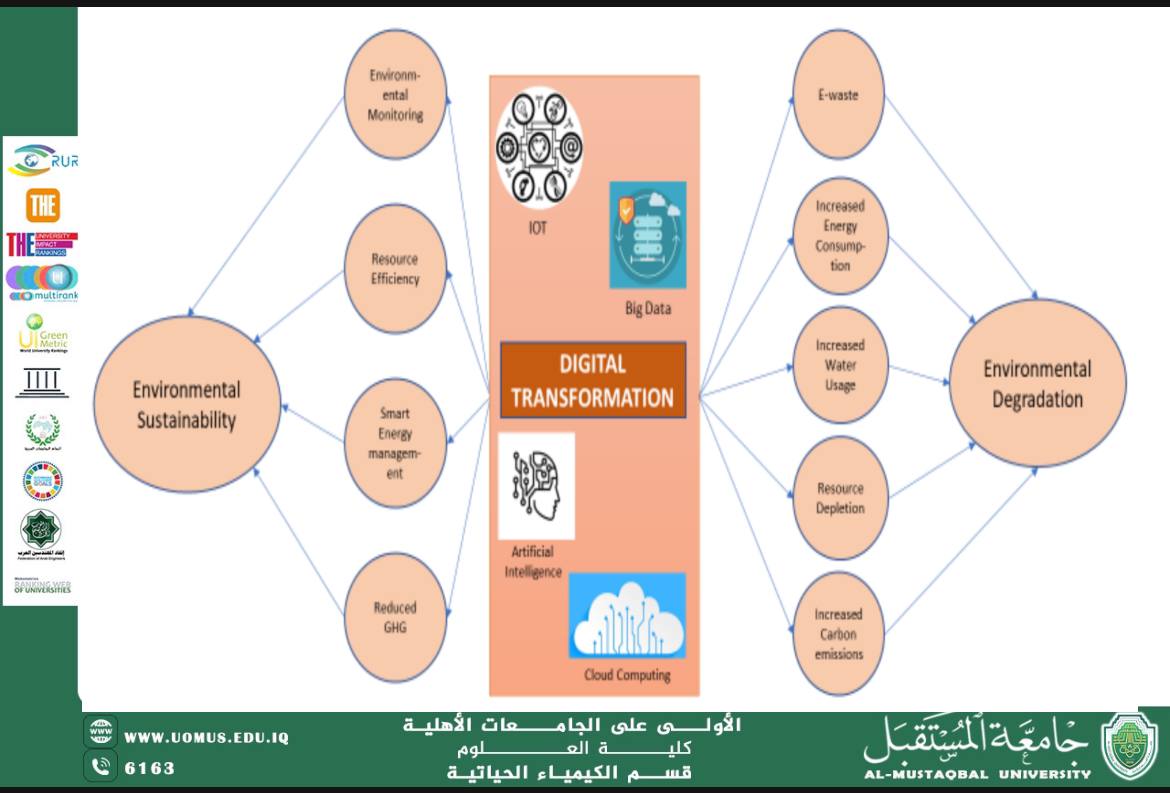
In the current digital age, digital transformation has become an essential part of growth and development worldwide. As digital technologies continue to advance, numerous digital risks have emerged, affecting individuals and societies. While these risks can pose threats to personal safety and cybersecurity, they also have a close relationship with sustainability goals, which aim to achieve sustainable development across economic, social, and environmental sectors.<br />Digital Risks<br />Digital risks are diverse and multifaceted, including cyberattacks, malware, data privacy concerns, risks associated with artificial intelligence, and privacy in digital environments. Some of the main digital risks include:<br />1. Cyberattacks and Breaches: Cyberattacks are one of the biggest digital threats, which can lead to breaches of personal or business data, resulting in significant financial losses for individuals and companies.<br />2. Big Data Abuse: With the growing use of big data technologies for collection and analysis, malicious actors can exploit personal information or manipulate data to serve their interests.<br />3. Artificial Intelligence Risks: While artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to enhance processes and foster innovation, it can also contribute to job displacement or exacerbate inequalities in access to services.<br />4. Digital Privacy: As internet usage increases, it becomes more difficult to maintain personal privacy. Individuals face the risk of personal information being leaked due to cybersecurity breaches.<br />Digital Risks and Sustainability Goals<br />The United Nations established the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015 as a global framework to achieve sustainable development in the long term. These goals include 17 main objectives, such as eradicating poverty, achieving gender equality, protecting the environment, and promoting quality education.<br />As digital transformation evolves, the relationship between digital risks and sustainability goals becomes increasingly significant:<br />1. Digital Justice and Bridging Economic Gaps:<br />o Digital risks, such as attacks on digital infrastructure, can reduce access to technology for poorer communities or remote regions. These digital divides may lead to the marginalization of communities lacking access to the internet and digital services.<br />o To achieve Goal 10 (Reducing Inequality Within and Among Countries), actions must be taken to protect individuals from digital risks, ensuring that digital transformation does not increase social and economic disparities.<br />2. Achieving Quality Education:<br />o Digital transformation in education requires the creation of a safe online environment for students and teachers, while ensuring the protection of data from cyberattacks. A breach or data leakage can undermine trust in digital systems and disrupt the educational process.<br />o To achieve Goal 4 (Quality Education), digital systems in schools and universities must be able to protect students' personal data and ensure the safe dissemination of knowledge.<br />3. Environmental Protection:<br />o Through technologies like environmental data analysis and artificial intelligence, sustainability practices in areas like energy management and resource conservation can be improved. However, the large energy consumption of cloud computing and digital servers poses environmental risks.<br />o Developing sustainable technologies that consume less energy and reduce the environmental impact of digital operations is crucial to achieving Goal 13 (Climate Action).<br />4. Protecting Digital Rights and Privacy:<br />o In the age of the internet, digital privacy and data protection are critical human rights concerns. Maintaining privacy and protecting digital rights are fundamental components of Goal 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions).<br />o These efforts require strict regulations to safeguard personal data, ensuring that digital systems allow users to control their information without manipulation or exploitation.<br />Strategies to Address Digital Risks and Promote Sustainability<br />To address digital risks and achieve sustainability goals, several strategies can be employed:<br />1. Enhancing Digital Awareness: By raising awareness about how to protect personal data and sensitive information, digital risks can be minimized.<br />2. Encouraging Sustainable Innovation: Support for sustainable technological innovation that enhances the use of natural resources while minimizing environmental harm is essential, such as the development of green computing technologies.<br />3. Data Protection Legislation: It is crucial to establish laws and policies that protect privacy and individuals' rights in digital environments, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).<br />4. Investing in Cybersecurity: Adequate resources must be allocated to strengthen cybersecurity infrastructure, preventing attacks and protecting vital systems such as smart internet technologies.<br />At end, digital risks represent a significant challenge in the modern era. However, through effective strategies and innovative solutions, the impact of these risks on sustainability goals can be minimized. The integration of digital transformation and sustainability requires intelligent and cautious responses to ensure that technology remains a positive force for improving quality of life and protecting the planet.<br />Al-Mustaqbal University, the first university in Iraq.