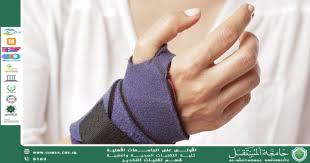
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome( CTS) is a condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway located at the base of the palm, formed by bones of the wrist and a ligaments.<br />This tunnel houses the median nerve and tendons responsible for moving the fingers .When pressure is applied to the median nerve .it leads to a variety of symptoms, typically affecting hand functions.<br />Causes:-<br />CTS develops when increased pressure within the carpal tunnel ,which can be due to various factors:-<br />1-repititive motion: Engaging in activities that require repetitive hand or wrist Such as typing, using mouse, assembly line work , can irritant the tendons and compress the median nerve.<br />2-Injury or trauma: fracture or sprain in the wrist can lead to swelling that puts pressure on the median nerve.<br />3-Hormonal changes:- pregnancy , menopause and other hormonal fluctuations can leads to fluid retention, which may increase pressure in tunnel .<br />4-Healtrh conditions:- conditions such as diabetes, rheumatic arthritis , thyroid problem and obesity can increase the risks of developing CTS.<br />5-Anatomical factors: Some people may have a naturally smaller carpal tunnel , making them more prone to compression.<br />Symptoms:-<br />1-Numbness and tingling:- often felt in the thumb, index and middle finger, which may worse at night.<br />2-Pain:- A dull ach or sharp pain in the wrist , hand, forearm which can extend up to the shoulder in some cases.<br />3-Weakness:- Difficulty gripping objects or performing tasks that require dexterity, such as buttoning a shirt or holding a pen. <br />4-Clumsiness:- A felling dropping things due to reduced hand strength and coordination.<br />Diagnosis:-<br />1-physical examination:-This involves and performing specific(e.g Tinels sign and phalens maneuver) to check for nerve compression.<br />2-Electrodiagnosis tests:- These include nerve conduction studies and electromyography(EMG), which help determine the degree of compression.<br />3-Imaging tests:- in some cases ultrasound or MIR scans may be used to rule out other causes of symptoms.<br />Treatment:-<br />1-NON- surgical treatments:- This include the following<br /> A-Rest: Taking breaks from repetitive activities to allow the wrist to recover.<br />B-Wrist splint: Wearing splint ,especially at night, to keep the wrist in a neutral position and prevent further irritation of the median nerve.<br />C-Anti- inflammatory medication:- non steroid anti- inflammatory drug (NSAID) can reduce swelling and relieve pain<br />D- corticosteroid injections:- to reduce inflammation and swelling around the carpal tunnel.<br />E-Physical therapy:- Exercises to stretch and strengthen the wrist and muscles.<br />2- surgical treatment:-If non-surgical treatments are ineffective and symptoms are severe ,surgery may be needed .the most common procedure is carpal tunnel release surgery where the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel is cut to relieve pressure on the median nerve either traditional open method or minimum invasive endoscopic techniques.<br />Prevention :-There are certain measure can help reduce the risk of developing the condition through:-<br /> 1- Take frequent breaks: This is happen by taking regular break to rest the hand and wrist in repetitive wrist movements.<br /> 2- Proper ergonomics: During the work station the wrists must be in neutral position( not bent upward or downward )while typing or using mouse.<br /> 3- Exercises for the hand and wrists :- Stretching and strengthening exercises can help maintain flexibility and reduce the risks of strain <br /> 4- Maintain a healthy weight :- this can reduce pressure on the nerve and improve overall joint health<br />د طالب جيجان طاهر<br />Al-Mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq<br />