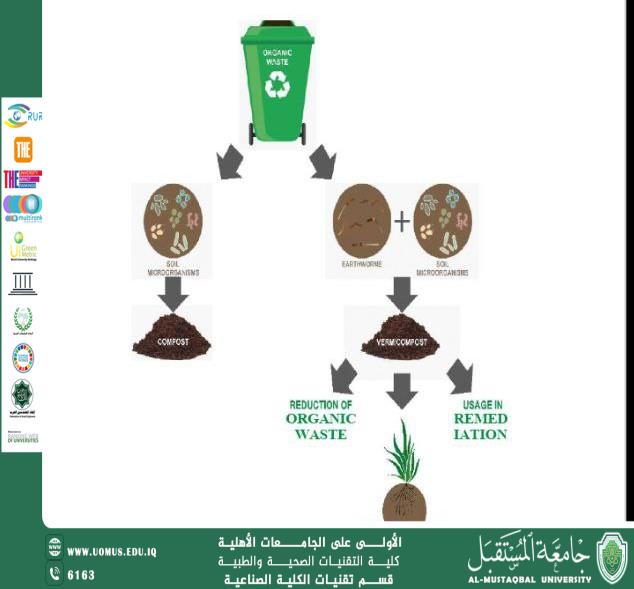
The role of earthworms in recycling organic waste and producing Vermicompost
Anssam F. Agah<br />Bachelor's of Biology / Microbiology<br /><br />Introduction:<br /><br />• Earthworm:<br />Earthworms are an environmentally significant group of invertebrates that provide many essential ecosystem services. They decompose plant and animal matter, contribute to soil formation, improve soil properties, and increase fertility. They also serve as a food source for various animals. Earthworms belong to the class Oligochaeta , which contains 16 different families, the most important of which is the Lumbricidae family. The role of earthworms in soil has been known for over a century, with significant contributions to soil formation, physical and chemical weathering processes, soil differentiation, and the creation of surface soil. Their burrows enhance soil fertility and promote plant growth. Earthworms also bury organic matter, enrich the soil with mineral elements, and contribute to the global cycle of erosion, sedimentation, and the transport of fine particles to the soil surface via hydrological and atmospheric means.<br /><br />Earthworm species vary greatly in size, diet, reproductive rate, and habitat preferences. Researchers classify earthworm environments into three groups based on their activity in the soil:<br />1. Epigeic worms: These are small, fast-reproducing worms found in the topsoil layer, typically at depths of 0-30 cm.<br />2. Endogeic worms: These dig horizontal, transient burrows, are pale in color, and live at depths of up to 60 cm.<br />3. Anecic worms: These large worms have dark-colored anterior bodies and create vertical burrows that can last for several years, often exceeding two meters in depth.<br /><br />In addition to contributing to soil formation and differentiation over time, earthworms enhance soil fertility by burying organic material and enriching the soil with both macro and micro-minerals. They also foster the growth of beneficial soil bacteria through selective feeding, releasing beneficial microbes into the soil through their digestive castings. This process improves the physical, chemical, and biological properties of the soil, ensuring its cleanliness and sterilization. Earthworms act as bio-control agents that help combat and suppress various soil pathogens, contributing to the nitrogen and carbon cycles in the soil and climate.<br /><br />• Vermicompost:<br />Vermicompost is a fertilizer rich in macronutrients (N, P, K), calcium, magnesium, and micronutrients (Fe, Mn, Zn), as well as beneficial soil microorganisms such as actinomycetes and nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Azotobacter, Azospirillum, Nitrobacter , Rhizobium), phosphorus-fixing bacteria (Pseudomonas sp.) , and Trichoderma . It improves nutrient availability for plants and increases their uptake. Vermicompost is also rich in humates and growth regulators like auxins, cytokinins, and gibberellins, which support plant growth and enhance disease resistance. It contains enzymes such as chitinase, cellulase, lipase, urease, phosphatase, and dehydrogenase, which enhance soil fertility and improve its physical, chemical, and biological properties.<br /><br />Uses of Vermicompost: It helps in treating heavy metal toxicity, increasing plant productivity, controlling pests and pathogens, and recycling organic waste.<br /><br />Objective:<br />1. Reducing environmental pollution by using organic household waste (food scraps, paper waste, and other organic waste).<br />2. Vermicompost is a significant revolution in achieving sustainable development goals, particularly Goal 13 (Climate Action) and Goal 15 (Life on Land).<br />3. Increasing soil fertility and combating plant diseases and pests.<br />4. Vermicompost can be considered an economic resource.<br /><br />Conclusion:<br />Earthworms play a vital role in recycling organic materials and converting them into nutrient-rich compost through the vermicomposting process. This process not only improves soil quality and fertility but also contributes to reducing organic waste and protecting the environment from pollution. By utilizing this natural and effective technique, we can create a sustainable and healthy environment for future generations. Therefore, vermicompost is an essential step toward a greener and safer agricultural future.