مقالة بعنوان "Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)"للمهندس محمد عبد الكريم رزوقي
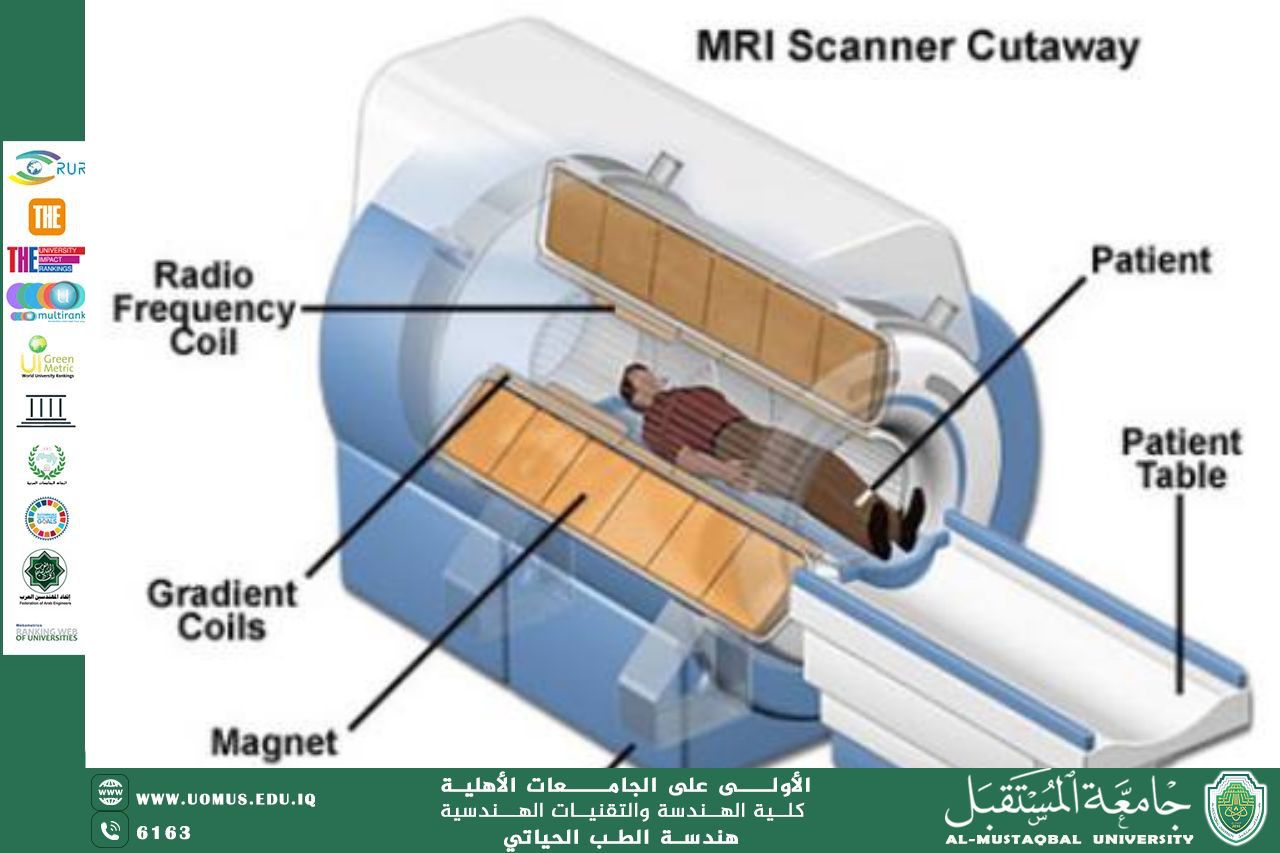
What is an MRI and where is it used?<br /><br />Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues in your body.<br />Most MRI machines are large, tube-shaped magnets. When you lie inside an MRImachine, the magnetic field inside works with radio waves and hydrogen atoms in your body to create cross-sectional images — like slices in a loaf of bread.<br /><br />Why it's done<br />MRI is a noninvasive way for a medical professional to examine your organs, tissues and skeletal system. It produces high-resolution images of the inside of the body that help diagnose a variety of conditions.<br />MRI of the brain and spinal cord<br />MRI is the most frequently used imaging test of the brain and spinal cord. It's often performed to help diagnose:<br />Aneurysms of cerebral vessels.<br />Conditions of the eye and inner ear.<br />Multiple sclerosis.<br />Spinal cord conditions.<br />Stroke.<br />Tumors.<br />Brain injury from trauma.<br /><br />MRI of the heart and blood vessels<br />MRI that focuses on the heart or blood vessels can check:<br />Size and function of the heart's chambers.<br />Thickness and movement of the walls of the heart.<br />Extent of damage caused by heart attacks or heart disease.<br />Structural problems in the aorta, such as aneurysms or dissections.<br />Inflammation or blockages in the blood vessels.<br />MRI of other internal organs<br />MRI can check for tumors or other irregularities in many organs in the body, including the following:<br />Liver and bile ducts.<br />Kidneys.<br />Spleen.<br />Pancreas.<br />Uterus.<br />Ovaries.<br />Prostate.<br />MRI of bones and joints<br />MRI can help look for:<br />Joint issues caused by traumatic or repetitive injuries, such as torn cartilage or ligaments.<br />Disk problems in the spine.<br />Bone infections.<br />Tumors of the bones and soft tissues.