An article titled "Molecular Study on the AcrAB, OqxAB, and MarA Genes of Escherichia Coli" by lecturer Nour Sabah Jabr
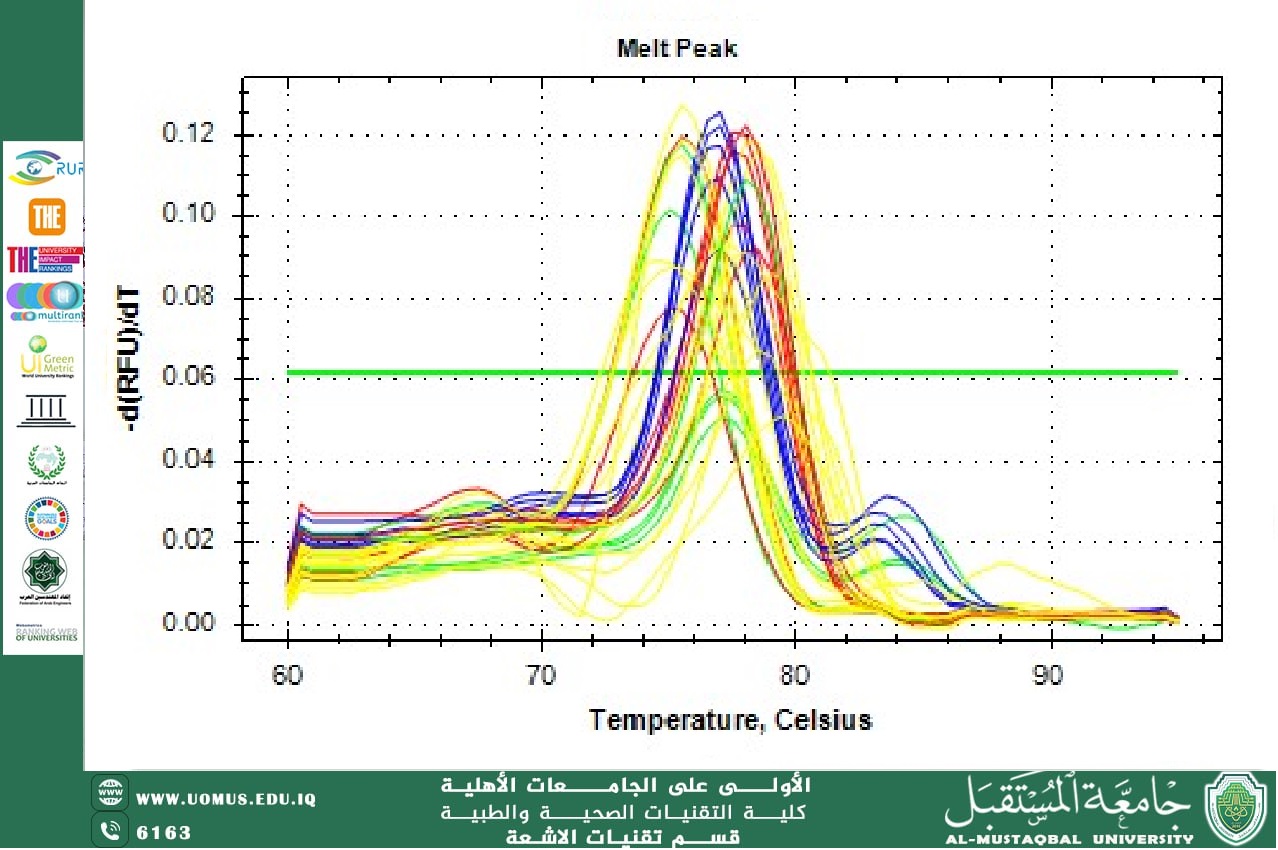
Molecular study on acrAB, oqxAB, and marA genes of Escherichia coli<br /> <br />The most frequent Gram-negative bacterium that causes urinary tract infections is Escherichia coli, recognized as an opportunistic pathogen. E. coli strains account for more than 85% of UTI cases. This study's goal is to identify the efflux pump genes (acrAB, oqxAB, and marA) that were isolated from a variety of UTI patients under the supervision of a specialist physician at two healthcare facilities, AL-Diwaniyah General Teaching Hospital and Maternity and Pediatrics Teaching Hospital in the AL-Diwaniyah city, Iraq. The study investigated the prevalence of E. coli which causes UTIs which included 200 urine samples from individuals with urinary tract infection (UTI) ranging in age from 5 to 62 years, which were tested for bacterial infection. Cultures of urine samples isolated from 200 suspected patients with urinary tract infection (UTI) on blood and MacConkey agar and confirmed by Vitek-2 system. Our results show that only 50 (39%) have been positively diagnosed with E. coli out of 200 patients, and an antibiotic sensitivity test was performed using the same system. AcrAB, oqxAB, and marA are efflux pump genes expressed using real-time PCR. The study revealed that 50 (100%) of the E. coli isolates had a high rate of oqxAB gene expression (15.22%), while the ratios of acrAB and marA genes were 5.88% and 4.03%, respectively. In conclusion, the majority of E. coli isolates studied were obtained from individuals suffering from multiple drug resistance (MDR) urinary tract infections. <br />Antibiotic susceptibility test <br /> The Vitek system(BioMeneux, Turkey) is a widely used automated system for performing antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) on bacteria. Here's a general overview of the protocol, but refer to your specific instrument's manual for detailed instructions: Vitek instrument, appropriate Vitek test card for the bacteria being tested (e.g., GN card for gram-negative bacteria), isolated bacterial colony, sterile saline solution and McFarland standards for inoculum standardization .<br />Quantitative Reverse Transcription Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)<br /> Drug-resistant E. coli isolates' efflux pump gene expression was measured using the quantitative Real-Time PCR method, with a housekeeping gene used as a reference. The strategy adhered to the steps described in the research .<br />Total RNA extraction<br /> Total RNA was extracted from MDR E. coli isolates using (Total RNA Extraction Kits) using the following procedures, which were adhered to precisely as prescribed by the manufacturer: Following the injection of 2µg/ml of inducible ethidium bromide into bacterial isolates on Luria Bertani broth and an incubation period at 37ºC to generate bacterial cells (OD600:0.8-1.0), Centrifuging the bacterial cells for a minute at 10,000 rpm yielded the supernatant, which was then collected. (1 ml) of Trizol reagent was added to the bacterial pellets, and they were violently vortexed for ten seconds at room temperature. <br /> After adding 200 μl of chloroform to each tube, they were shaken vigorously for a minute. The mixture was incubated on ice for five minutes. Centrifuged for fifteen minutes at 13,000 rpm at 4C°. 500μl of isopropanol was added to a new 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube containing the supernatant. Once the mixture has been integrated, turn the tube four or five times and leave it at 4C° for ten minutes. Centrifuged for 10 minutes at 4C° and 13,000 rpm.<br /> Once again, the supernatant was discarded, and (1 ml) of 80% ethanol was added and vortexed. Next, centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4 C°. The RNA pellet was allowed to air dry while the supernatant was disposed of. The extracted RNA sample was stored at -80°C after the RNA pellet was dissolved in each sample using 100 µl of free nuclease water.<br /><br />The Real-Time PCR primers: This study used NCBI-Gene bank sequence and Primer3 plus to construct Real-Time PCR primers to detect and quantify efflux pump genes in E. coli isolates. All primers were designed by the Iraqi Scientific Researcher Company using primer-3 plus<br />Results<br />The total number of urine samples was 200 samples, coming from different ages and genders, as the current study showed that 126 isolates (63%) had positive diagnostic results for infection with bacteria out of the 200 samples and that 50 isolates (39.7%) were the percentage of infection with E.coli bacteria. The rest of the percentages were due to other types of bacteria. The current study showed that all E.coli isolates were resistant to antibiotics and contained efflux pump genes. The purified real-time PCR products for DNA extraction of E.coli isolates by using gapA gene.<br /><br />