Scientific article by Assist lecturer Esraa Saleh Kamel:-Cloud Computing and its importance in Healthcare
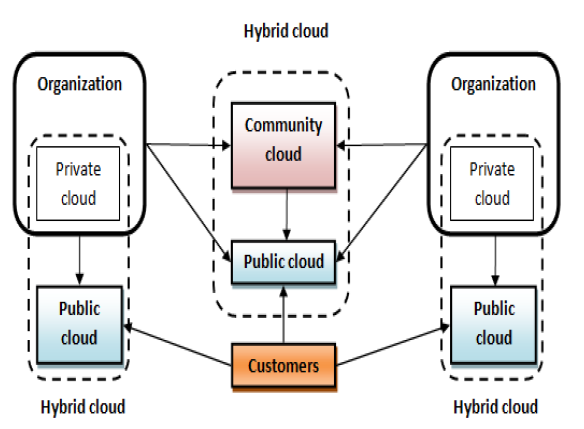
<br />Cloud Computing and its importance in Healthcare<br /><br /> Cloud computing environment provides a great flexibility and availability of computing resources at a lower cost. This emerging technology opens a new era of e-services in different disciplines. There are examples for cloud services provided by the most common Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, HP, and Sales force There are innovative applications for cloud computing in e-learning, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and e-governance. <br /> Cloud computing is a topic that received a great deal of attention by individuals and organizations from different disciplines in the last decade. Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) (e.g., Google, Microsoft, Amazon) are vendors who lease to their customers of cloud computing resources and services that are dynamically utilized based on customer’s demand according to a certain business model. The services are generally classified into three classes known as cloud service models:<br /><br /> Software as a Service (SaaS): In this model, CSPs are responsible for running and maintaining application software, operating system and computing resources. The services and complete software applications are delivered over the Internet and are accessed via a web browser.<br /> Customers can access hosted applications such as Gmail and Google Docs through different client devices such as laptops, iPads and cell phones. The customer does not need to buy licenses, install, upgrade, maintain or run software on his own computer. <br />Examples of SaaS providers are Zoho, Google Apps and Salesforce.com.<br /><br /> Platform as a Service (PaaS): In PaaS, a CSP provides, runs and maintains both system software (i.e., the operating system) and computing resources. The customer manages and runs the application software under the operating system and on the virtual resources provided by the CSP. Examples of PaaS providers are windows Azure, Google Apps Engine and Aptana cloud.<br /><br /> Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): In this model, the CSP provides a set of virtualized computing resources (e.g., network bandwidth, storage capacity, memory, processing power) in the cloud. It is the responsibility of the customer to run and maintain the operating system and the software applications on these virtual resources. Examples of IaaS providers are Drop Box, Amazon EC2 and Akamai. <br /><br />Cloud computing systems are classified as public cloud, private cloud, community cloud and hybrid cloud. These classes are known as deployment models and they describe the scope of services offered on the cloud to the customers.<br /><br />• Public Cloud: In public clouds the infrastructure and other cloud services are made available to the general public over the Internet. The cloud is owned and managed by a CSP who offers services to consumers on a pay-per-use basis. services are public including Amazon EC2, Google App Engine and Salesforce.com. <br /><br />Private Cloud: In private clouds the computing resources are operated exclusively by one organization. It may be managed by the organization itself or a CSP. Private clouds are considered to be more secure than public clouds since their users are trusted individuals inside the organization. <br /><br />Community clouds: Community clouds are similar to private clouds but the cloud infrastructure and computing resources are shared by several organizations that have the same mission, policy and security requirements. An example of a community cloud is the educational cloud used by universities and institutes around the world to provide education and research services.<br /><br />Hybrid Clouds: In hybrid clouds, the cloud infrastructure consists of a combination of two or more public, private or community cloud components. The cloud components are bound together by standardized technology and managed as a single unit, yet each cloud remains a unique entity. Hybrid clouds allow organizations to optimize their resources, so the critical core activities can be run under the control of the private component of the hybrid cloud while other auxiliary asks may be outsourced to the public component. Figure 2 below shows different cloud deployment Models.<br /><br /><br /><br />How Cloud Computing is Transforming the Healthcare Industry?<br />Moving over to the cloud has two-fold benefits. It has proven to be advantageous for both healthcare providers as well as the patients. Here are the ways cloud consulting is impacting healthcare.<br />Lowering of Costs<br />Cloud computing also provides the optimum ergonomic environment for scaling which is a desirable quality in the current times. With patient data flowing in not just from the records in the form of EMRs but also through the plethora of healthcare apps and health wearables, a cloud-based environment proves to be perfect for scaling and undergoing capacitive overhaul while keeping the costs in check.<br />Ease of Interoperability<br />Having the patient’s data in the cloud also promotes interoperability among the various segments of the healthcare industry- pharmaceuticals, insurance, and payments. This allows for a seamless transfer of data between the different stakeholders thus accelerating healthcare delivery and introducing efficiency in the process.<br />Access to High Powered Analytics<br />Performing analytics on patient data also can pave the way for formulating more personalized care plans for patients on an individual level. It also ensures that all the pertinent patient details are on record and nothing gets missed out when prescribing treatments. Cloud-based data analysis comes in handy when extracting relevant patient information.<br />Patient’s Ownership of Data<br />Patient records and medical images can be easily archived and retrieved when storing data on the cloud. While cloud security remains a concern, the reliability of cloud for data storage is definitely higher. Data redundancy is reduced with an increase in system uptime. <br />References:<br />[1] https://www.healthitoutcomes.com/doc/ways-cloud-computing-is-impacting-healthcare-0001<br />[2] Ahmed E. Youssef, " Exploring Cloud Computing Services and Applications", Journal of Emerging Trends in Computing and Information Sciences, VOL. 3, NO. 6, 2012.<br />