Cetane Number of Diesel Fuel
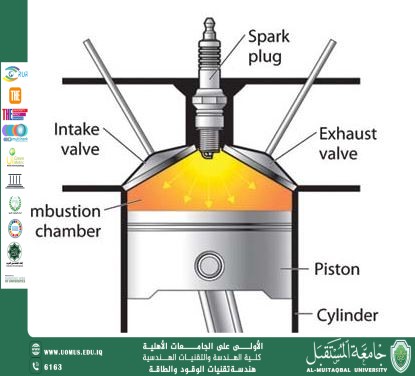
SDG 3 God Health and Wellbeing<br />SDG 12 Responsible Consumption and production<br />SDG 7 Affordable and clean Energy<br />Cetane Number of Diesel Fuel <br />Dr. Malik Mustafa Mohammed<br />1. Introduction <br />The cetane number (CN) is a critical parameter used to evaluate the ignition quality of diesel fuel. It measures how quickly and efficiently diesel fuel ignites under compression in a diesel engine. A higher cetane number indicates better ignition performance, leading to smoother combustion, reduced engine knocking, and lower emissions. <br /><br />This report examines the cetane number of diesel fuel, its significance, factors affecting it, and its impact on engine performance. <br /><br />2. Cetane Number: Definition and Measurement <br />- The cetane number is measured on a scale where: <br /> - Cetane (n-Hexadecane, C₁₆H₃₄) is assigned a value of 100 (excellent ignition quality). <br /> - Heptamethylnonane (HMN, C₁₅H₃₄) is assigned a value of 15 (poor ignition quality). <br />- The cetane number of a diesel fuel is determined by comparing its ignition delay (time between injection and combustion) to a reference blend of cetane and HMN in a standardized engine test (ASTM D613 or ISO 5165). <br /><br />Typical Cetane Numbers for Diesel Fuels <br />| Fuel Type | Cetane Number Range | <br />|-------------------------|--------------------| <br />| Standard Diesel (ULSD) | 48 – 55 | <br />| Premium Diesel | 50 – 60+ | <br />| Biodiesel (B100) | 48 – 65 | <br />| Synthetic Diesel (GTL) | 70 – 80 | <br /><br />3. Importance of Cetane Number in Diesel Engines <br />A higher cetane number improves: <br />✔ Cold Starting – Easier ignition in low temperatures. <br />✔ Combustion Efficiency – Reduced ignition delay, leading to smoother engine operation. <br />✔ Fuel Economy – More complete combustion improves mileage. <br />✔ Emissions Control – Lower NOx, CO, and particulate matter (PM) emissions. <br />✔ Engine Longevity – Less knocking and wear on engine components. <br /><br />A low cetane number (< 40) can cause: <br />❌ Hard starting (especially in cold weather). <br />❌ Excessive engine knocking. <br />❌ Increased smoke and emissions. <br />❌ Poor fuel efficiency. <br />-<br /><br />4. Factors Affecting Cetane Number <br />a) Chemical Composition <br />- Paraffins (Alkanes) → High CN (e.g., cetane = 100). <br />- Aromatics & Olefins → Low CN (poor ignition quality). <br />- Branched Hydrocarbons→ Lower CN than straight-chain hydrocarbons. <br />b) Additives & Blending <br />- Cetane Improvers (e.g., 2-Ethylhexyl nitrate, EHN) boost CN by 3-8 points. <br />- Biodiesel Blends (B5-B20) often increase CN due to their high oxygen content. <br /><br />(c) Refining Processes <br />- Hydrocracking produces high-CN diesel. <br />- Catalytic Cracking yields lower-CN diesel (requires additives). <br />5. Comparison with Octane Number (Gasoline) <br />| Property | Cetane Number (Diesel) | Octane Number (Gasoline) | <br />|-------------------|-----------------------|--------------------------| <br />| Measures | Ignition delay (shorter = better) | Knock resistance (longer = better) | <br />| Ideal Range | 50 – 60 | 87 – 93 (Regular – Premium) | <br />| Reference Fuels | Cetane (100), HMN (15) | Isooctane (100), n-Heptane (0) | <br />| Impact of High Value | Faster ignition, smoother combustion | Slower ignition, resists knocking | <br />6. Regulatory Standards for Cetane Number <br />Different countries have minimum cetane requirements for diesel: <br />- USA (ASTM D975) → Min. CN ≥ 40 (typically 48-50 for ULSD). <br />- EU (EN 590) → Min. CN ≥ 51. <br />- India (BS-VI) → Min. CN ≥ 51. <br />- China (GB 19147) → Min. CN ≥ 49. <br />7. Conclusion & Recommendations <br />- Diesel fuels with higher cetane numbers (50-60) provide better performance, efficiency, and lower emissions. <br />- Cetane improvers and biodiesel blending can enhance CN in low-quality diesel. <br />- Regulatory compliance ensures optimal diesel quality for modern engines. <br />Recommendations: <br />✔ Use premium diesel (CN > 50) for better engine performance. <br />✔ Consider cetane boosters in regions with poor-quality diesel. <br />✔ Follow engine manufacturer guidelines for optimal fuel selection. <br />References<br />- ASTM D613 (Standard Test Method for Cetane Number) <br />- EN 590 (European Diesel Fuel Standards) <br />- U.S. EPA Diesel Fuel Regulations <br />- SAE Technical Papers on Diesel Combustion <br />Al-Mustaqbal University The First University in Iraq<br />