Affordable and Clean Energy: Progress, Challenges, and Pathways Forward
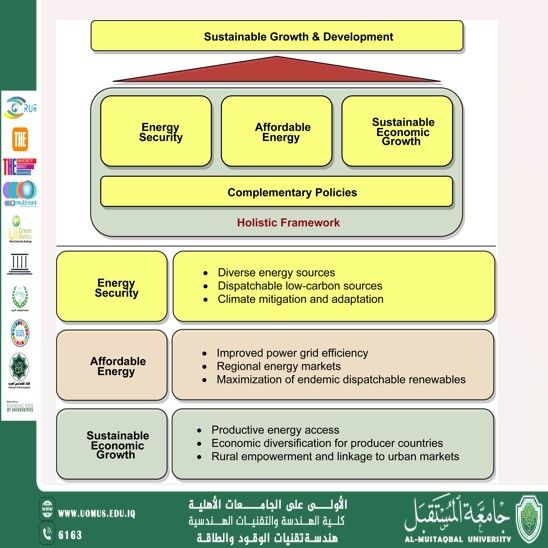
SDG 7 Affordable and Clean Energy<br />SDG 11 Sustainable cities and Communities<br />Sustainable Development Goal 7<br />Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7) in Iraq<br />Affordable and Clean Energy: Progress, Challenges, and Pathways Forward<br />Dr. Malik Mustafa Mohammed<br />Introduction <br />Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7) aims to ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy by 2030. For Iraq, a country endowed with vast oil reserves but plagued by decades of conflict and institutional instability, achieving SDG 7 is critical to addressing energy poverty, reducing environmental degradation, and fostering economic resilience. This report examines Iraq’s progress toward SDG 7, highlights key challenges, and proposes actionable recommendations.<br />Current Energy Landscape <br />1. Energy Production and Consumption <br /> - Iraq relies heavily on fossil fuels, with oil accounting for over 99% of its energy mix. Despite being the second-largest oil producer in OPEC, outdated infrastructure and inefficiencies result in significant energy losses. <br /> - Electricity generation capacity is insufficient, with frequent blackouts forcing reliance on imported power (20% from Iran and Turkey) and private generators. <br />2. Access to Electricity <br /> - Approximately 90% of Iraq’s population has grid access, but reliability remains a major issue. Rural areas, particularly in the south and Kurdish regions, experience lower access and poorer service quality. <br />3. Renewable Energy Potential <br /> - Iraq has immense solar potential (2,000–2,500 kWh/m²/year) and wind resources in the west, yet renewables contribute less than 1% to the energy mix. <br />Progress Toward SDG 7<br />1. Renewable Energy Initiatives<br /> - The government has set a target of 20% renewable energy by 2030. Pilot projects include the 500 MW Solar Park in Muthanna Governorate, supported by the UAE, and smaller off-grid solar installations in rural areas. <br /> - The World Bank’s Iraq Energy Sector Support Project aims to modernize infrastructure and integrate renewables. <br />2. Energy Efficiency Efforts <br /> - Programs to reduce gas flaring in the oil sector (a major source of CO₂ emissions) and improve grid efficiency are underway, though progress is slow. <br />3. International Collaboration <br /> - Partnerships with UNDP, the European Union, and private firms like TotalEnergies are advancing solar and gas capture projects. <br />Key Challenges <br />1. Infrastructure and Governance <br /> - Aging infrastructure, underinvestment, and corruption hinder energy sector reforms. <br /> - Political instability and bureaucratic delays deter foreign investment. <br />2. Economic Barriers <br /> - Over 90% of government revenue comes from oil, creating fiscal dependency and disincentivizing renewable transitions. <br />3. Environmental and Social Issues <br /> - Gas flaring and water-intensive fossil fuel operations exacerbate environmental degradation and public health crises. <br /> - Energy subsidies strain public finances while failing to address equitable <br />Case Study: Solar Energy in Rural Areas<br />In the Kurdish region, NGOs like Mercy Corps have deployed solar microgrids, providing reliable electricity to off-grid communities. These projects demonstrate scalable solutions for rural electrification and job creation. <br />Recommendations <br />1. Policy and Investment <br /> - Accelerate renewable energy targets and incentivize private sector participation through tax breaks and streamlined regulations. <br /> - Redirect fossil fuel subsidies toward renewable infrastructure and energy efficiency programs. <br />2. Capacity Building <br /> - Train local engineers and technicians in solar and wind technologies to build a skilled workforce. <br />3. Regional and International Cooperation<br /> - Strengthen partnerships with Gulf states and international agencies to secure funding and technical expertise. <br />4. Community Engagement <br /> - Promote decentralized renewable systems to empower marginalized regions and reduce urban-rural disparities. <br />Conclusion <br />Achieving SDG 7 in Iraq requires a transformative shift from fossil fuel dependency to sustainable energy systems. While challenges persist, Iraq’s renewable potential and recent initiatives offer hope. Prioritizing inclusive policies, international collaboration, and innovative financing can pave the way for a resilient energy future, aligning with broader SDGs such as climate action (SDG 13) and economic growth (SDG 8). <br />Data Sources: World Bank (2023), UNDP Iraq Reports, International Energy Agency (IEA), and Iraq’s Ministry of Electricity.<br />Al-Mustaqbal University The First University in Iraq<br /><br />