Products Derived from Crue Oil: A Comprehensive
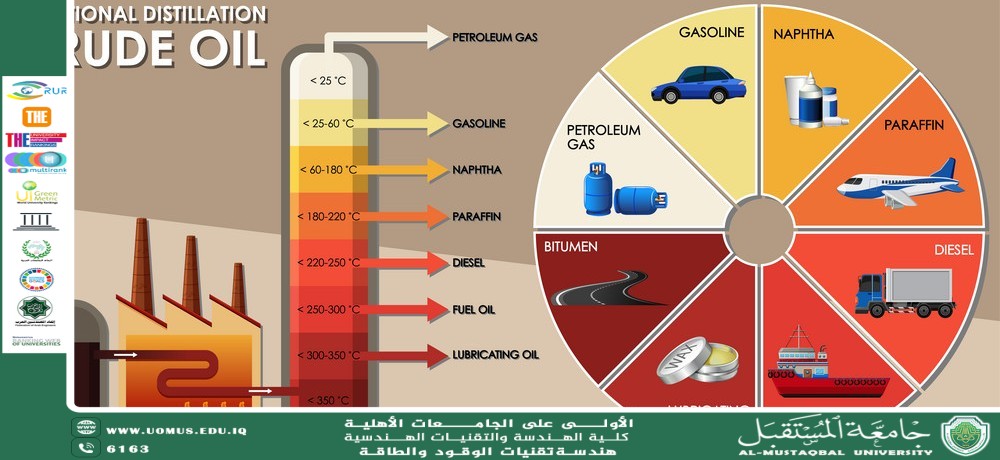
SDG 9 Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure<br />SDG 15 Life on Land <br />Dr. Malik Mustafa Mohammed<br />Products Derived from Crue Oil: A Comprehensive<br />Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons that undergoes refining to produce a wide range of valuable products. These products are categorized based on their boiling points, chemical compositions, and applications. Below is a detailed breakdown of the major products obtained from crude oil refining. <br />1. Petroleum Gases (LPG & Light Ends) <br />- Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) – Propane & butane used for heating, cooking, and fuel. <br />- Ethane – Feedstock for petrochemicals (ethylene production). <br />- Methane (Natural Gas) – Used for electricity generation and heating. <br />Applications:<br />✔ Domestic fuel (cooking, heating) <br />✔ Petrochemical feedstock <br />✔ Refinery fuel <br />2. Gasoline (Petrol) <br />- Light Distillate (Boiling Range: 30–200°C) <br />- Octane Rating: 87–93 (Regular to Premium) <br />- Types: <br /> - Regular Unleaded (87–90 octane) <br /> - Premium Gasoline (91–93+ octane) <br /> - Reformulated Gasoline (RFG) – Lower emissions <br /><br />Applications: <br />✔ Automobile fuel (spark-ignition engines) <br />✔ Small engines (lawnmowers, motorcycles) <br />3. Naphtha <br />- Intermediate Distillate (Boiling Range: 30–200°C) <br />- Two Types: <br /> - Light Naphtha – Used in gasoline blending. <br /> - Heavy Naphtha – Feedstock for petrochemicals (plastics, synthetic rubber). <br />Applications: <br />✔ Feedstock for ethylene crackers (plastics production) <br />✔ Solvents, paint thinners <br />✔ Gasoline blending <br />4. Kerosene & Jet Fuel <br />- Boiling Range: 150–300°C <br />- Types: <br /> - Kerosene (Paraffin Oil) – Used for lighting, heating, and aviation. <br /> - Jet A & Jet A-1– Aviation turbine fuel. <br />Applications: <br />✔ Aviation fuel (commercial & military jets) <br />✔ Heating oil (in some regions) <br />✔ Lamp oil (traditional use) <br />5. Diesel & Gas Oil <br />-Boiling Range:200–350°C <br />- Cetane Number:40–60 (measures ignition quality) <br />- Types: <br /> -Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) – Standard automotive diesel. <br /> - Heating Oil – Used in furnaces. <br /> - Marine Diesel (Bunker Fuel)– For ships. <br />Applications: <br />✔ Truck, bus, and car fuel (compression-ignition engines) <br />✔ Industrial & agricultural machinery <br /> Backup power generators <br /><br />6. Fuel Oil (Heavy Distillates & Residues) <br />Boiling Range: 350–600°C <br />-Grades:<br /> - No. 2 Fuel Oil – Diesel-like, used in heating. <br /> - No. 4 & No. 5 Fuel Oil – Industrial boilers. <br /> No. 6 (Bunker C) – Large ships & power plants. <br />Applications: <br />✔ Marine fuel (large vessels) <br />✔ Power plants (electricity generation) <br />✔ Industrial furnaces <br />7. Lubricating Oils & Greases <br />- Derived from Heavy Distillates <br />- Types: <br /> - Engine Oil (5W-30, 10W-40) <br /> - Gear Oil <br /> - Hydraulic Oil <br /> -Greases (Lithium-based) <br />Applications:<br />✔ Automotive engines <br />✔ Industrial machinery <br />✔ Aviation & marine engines <br />8. Bitumen (Asphalt) <br />- *Residue from Vacuum Distillation <br />- Used in: <br /> - Road construction <br /> - Roofing materials <br /> - Waterproofing <br />Applications: <br />✔ Paving roads & highways <br />✔ Roofing shingles <br />✔ Pipe coatings <br />9. Petroleum Coke (Pet Coke) <br />-Solid Carbon Residue from Cracking <br />- Types: <br /> - Fuel-Grade Coke – Used in power plants. <br /> - Anode-Grade Coke– Used in aluminum production. <br />Applications: <br />✔ Cement kilns (fuel) <br />✔ Aluminum smelting (electrodes) <br />10. Petrochemical Feedstocks <br />Crude oil derivatives are used to produce: <br />✔Plastics (Polyethylene, PVC, PET) <br />✔ Synthetic Rubber <br />✔ Fertilizers (Ammonia, Urea) <br />✔Solvents & Chemicals (Benzene, Xylene, Toluene) <br />Conclusion <br />Crude oil refining produces fuels (gasoline, diesel, jet fuel), lubricants, asphalt, and petrochemical feedstocks, making it indispensable for modern industry and transportation. Advances in refining (hydrocracking, catalytic reforming) continue to improve efficiency and product quality. <br /><br />Future Trends:<br />- Biofuel Blending(Biodiesel, Ethanol) <br />- Hydrogen & Synthetic Fuelfrom crude oil <br />- Carbon Capture in Refining <br />Al-Mustaqbal University The First University in Iraq<br /><br />