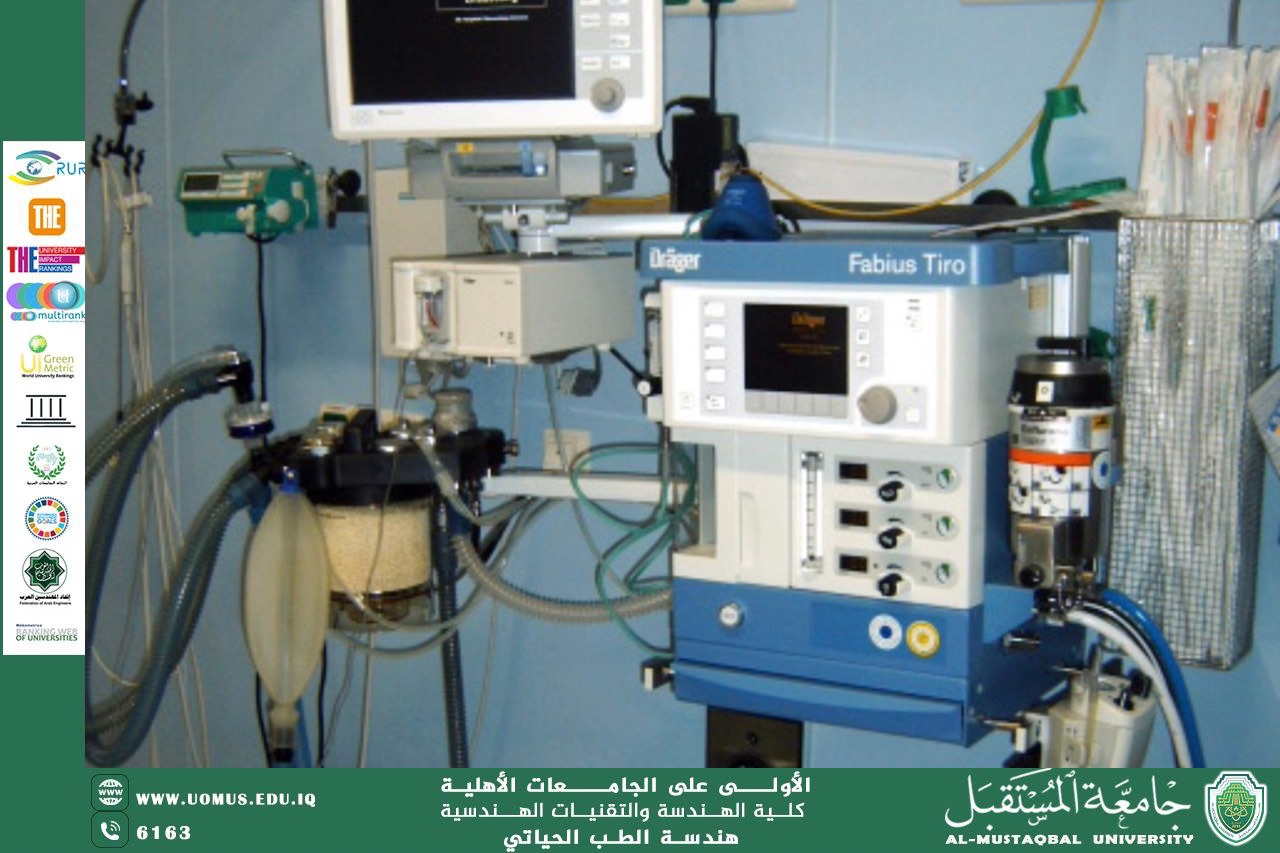
مقالة بعنوان " Anesthesia Machine"للدكتورة بتول علي نوري
The Anesthesia Machine: Function and Importance in Modern Surgery<br /><br />The anesthesia machine is a critical device used in modern medicine to deliver a precise and controlled mixture of gases to patients undergoing surgical procedures. Its primary function is to provide anesthetic agents and oxygen, ensuring the patient remains unconscious, pain-free, and stable throughout the operation.<br /><br />A standard anesthesia machine consists of several key components:<br /> 1. Gas delivery system – Supplies medical gases such as oxygen, nitrous oxide, and air.<br /> 2. Vaporizers – Convert liquid anesthetic agents (like isoflurane or sevoflurane) into vapors and add them to the gas mixture.<br /> 3. Breathing circuit – Delivers the gas mixture to the patient and removes exhaled carbon dioxide.<br /> 4. Ventilator – Assists or controls the patient’s breathing during general anesthesia.<br /> 5. Monitors – Track vital parameters such as oxygen saturation, heart rate, blood pressure, and end-tidal CO₂.<br /><br />Safety features are integrated into the anesthesia machine to prevent hypoxia and ensure accurate gas delivery. These include oxygen failure alarms, pressure gauges, flowmeters, and scavenging systems to eliminate excess anesthetic gases from the operating room.<br /><br />In conclusion, the anesthesia machine is an essential tool in surgical practice, playing a central role in patient safety and the success of operative procedures. Proper training and regular maintenance are vital to ensure its reliable performance.