Incineration at Residential Sites (Waste-to-Energy - WtE)
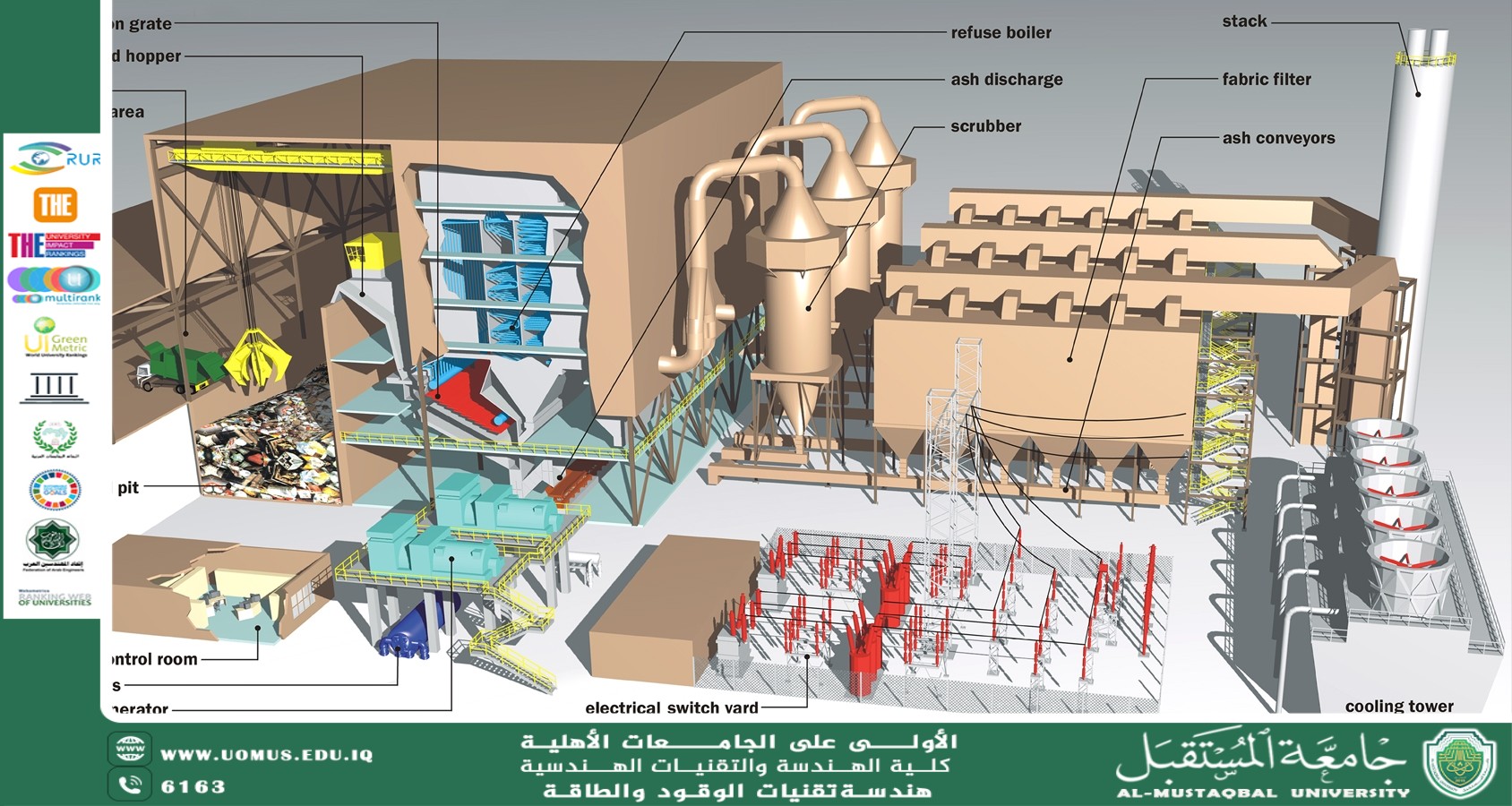
🔥 Incineration at Residential Sites (Waste-to-Energy - WtE)<br />By Dr. Malik Mustafa Mohammed<br />SDG 13 – Climate Action<br />SDG 7 – Affordable and Clean Energy<br />SDG 11 – Sustainable Cities and Communities<br />Incineration, when used as a waste-to-energy (WtE) method at the residential or small-community level, converts household waste into usable energy such as heat, electricity, or fuel. Though promising, implementing this system requires careful planning due to technical, environmental, and regulatory challenges.<br />1. 🔍 Understanding What You Burn<br />Not all waste is suitable for incineration. Acceptable materials include:<br />Organic waste (food scraps, yard trimmings)<br />Combustible items (paper, cardboard, untreated wood, textiles, some plastics)<br />Avoid burning hazardous waste like batteries, PVC, treated wood, or medical waste, as this can release toxic pollutants.<br />2. ⚙️ Choosing the Right Technology<br />For individual homes or small communities:<br />Pyrolytic stoves: High-temperature combustion with low emissions.<br />Gasifiers: Convert waste to syngas for energy.<br />Modular WtE systems: Compact and suitable for mixed waste.<br />FOr larger communities:<br />Centralized plants with boilers, turbines, and heat exchangers can provide electricity and district heating.<br />3. ⚡ Forms of Usable Energy<br />Incineration can provide:<br />Heat: Used for water and space heating.<br />Electricity: Generated via turbines or syngas-powered engines.<br />Cooking fuel: Through gasification.<br />4. 🌱 Environmental Considerations<br />Advantages:<br />Reduces landfill waste by up to 90%<br />Produces renewable energy<br />Cuts methane emissions from decomposing waste<br />Risks:<br />Air pollution (dioxins, NOx, SO₂)<br />Toxic ash requiring proper disposal<br />CO₂ emissions from fossil-based materials<br />Solution: Employ scrubbers, filters, and catalytic converters to control emissions.<br />5. 📜 Legal and Regulatory Requirements<br />Before installation:<br />Check local zoning laws and environmental regulations<br />Secure permits for air emissions and waste management<br />Follow national/international standards (e.g., EPA, EU directives)<br />6. 🔁 Integration with Other Methods<br />Incineration works best when combined with:<br />Anaerobic digestion for organic waste<br />Recycling programs for non-combustibles<br />Solar/wind systems for hybrid energy generation<br />7. 🌍 Real-World Applications<br />Sweden & Denmark: Centralized WtE plants for district heating<br />India & China: Rural biogas plants and gasification for cooking and lighting<br />Off-grid areas: Pyrolysis stoves used for cooking and minimal power<br />Al-Mustaqbal University The First University in Iraq<br /><br />