A scientific article by the teaching assistant (Nour Al-Huda Ahmed) entitled “Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in Training Doctors: Medical Simulation Without Borders”
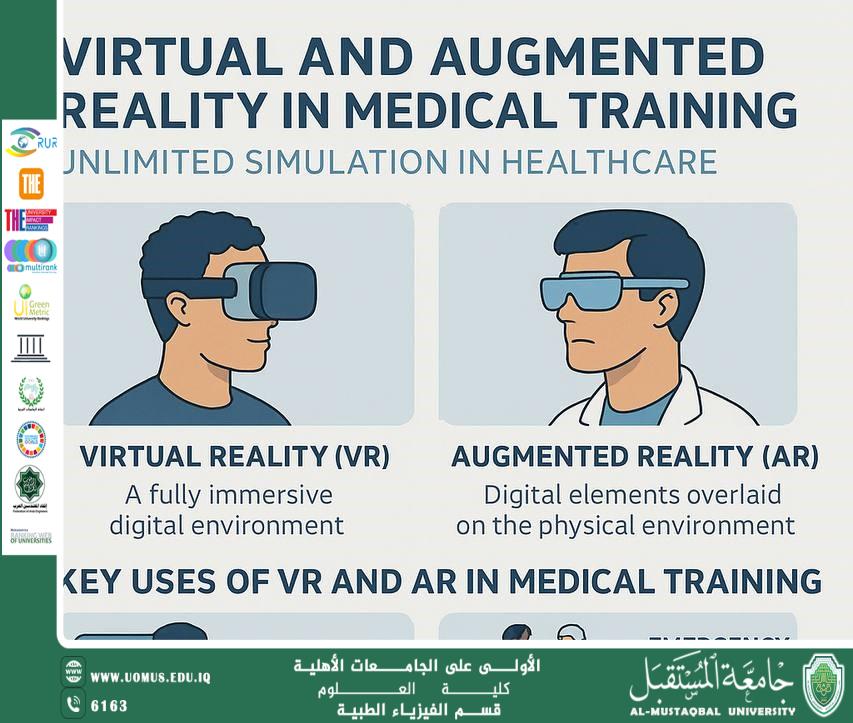
In an era of rapid innovation, Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have become some of the most transformative technologies in medical education. These tools are not just changing how doctors learn—they are creating a true revolution in simulating medical and surgical procedures, making training safer, more interactive, and highly precise.<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />What Are Virtual and Augmented Reality?<br /> • Virtual Reality (VR):<br />A technology that creates a fully immersive digital environment. Users wear a special headset and are transported into a 3D medical training scenario that feels real.<br /> • Augmented Reality (AR):<br />This technology overlays 3D digital information on the real physical environment using AR glasses or tablets. It allows doctors to visualize anatomical structures or procedures projected onto real patients or training models.<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Key Uses of VR and AR in Medical Training<br /> 1. Surgical Simulations:<br />Surgeons can practice complex procedures such as tumor removal or heart surgeries in a risk-free virtual setting before performing them on real patients.<br /> 2. Medical School Training:<br />Students can explore human anatomy in detailed 3D, improving comprehension and engagement in ways traditional textbooks cannot.<br /> 3. Emergency and Critical Care Scenarios:<br />Teams can rehearse life-threatening situations like cardiac arrest or severe bleeding in a controlled and interactive way to prepare for real-life pressure.<br /> 4. Remote Medical Collaboration:<br />With AR, experienced doctors can guide and assist colleagues remotely in real time, enhancing communication and knowledge sharing.<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Benefits of Using VR and AR in Medical Training<br /> • Reduce medical errors through safer practice environments.<br /> • Improve decision-making skills under stress.<br /> • Enable continuous training without needing live patients.<br /> • Provide a safe environment to learn from mistakes.<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Challenges in Adopting These Technologies<br /> • High cost of devices and software, especially in developing countries.<br /> • Need for high-quality educational content that is regularly updated.<br /> • Resistance to integrating new tech into traditional medical curricula.<br /> • Technical issues such as latency or limited model accuracy.<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Conclusion<br /><br />Virtual and augmented reality are no longer science fiction—they are powerful tools redefining how medical professionals are trained. As technology continues to advance and become more accessible, these solutions are expected to become essential in preparing the next generation of healthcare providers, offering realistic, hands-on learning—without real-world risks.<br /><br /><br /><br /><br />"AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq"<br/><br/><a href=https://uomus.edu.iq/Default.aspx target=_blank>al-mustaqbal University Website</a>