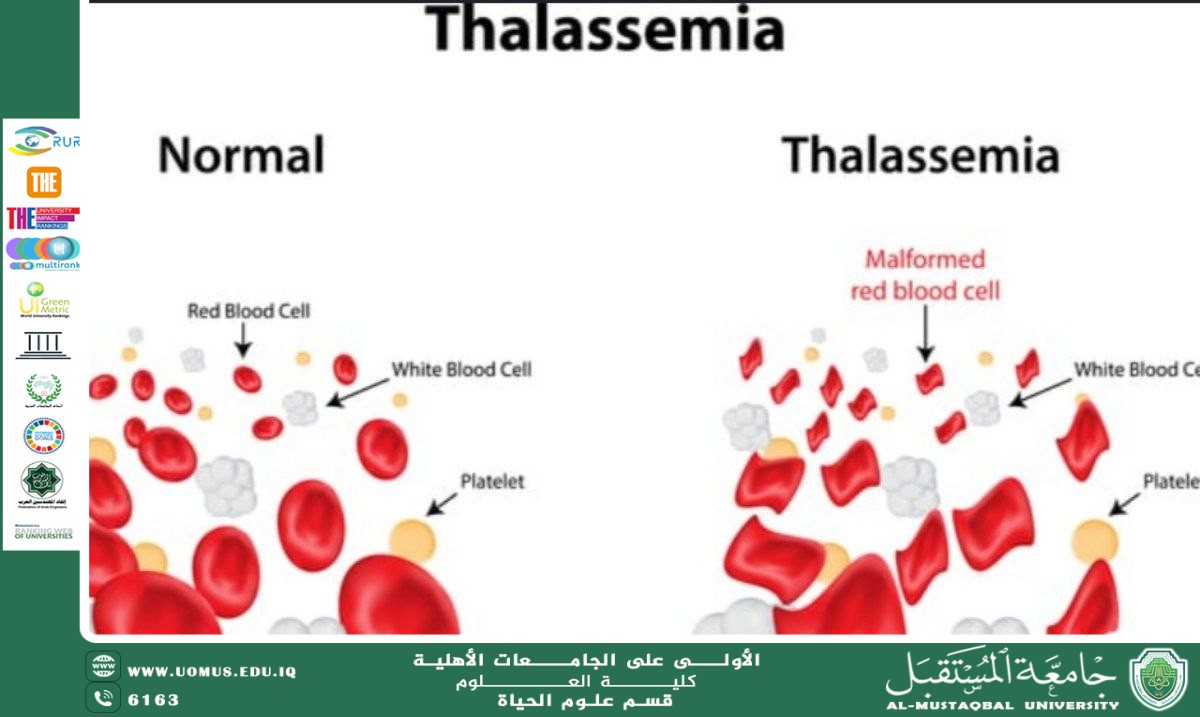
A scientific article by the teaching assistant, Ala Adel Rasmi, entitled "Thalassemia"
Thalassemia is a genetic disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. It is one of the most common hereditary blood diseases, especially in the Mediterranean region, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa.<br /><br />Types of Thalassemia<br />Thalassemia is divided into two main types, based on the protein chains affected:<br /><br />Alpha Thalassemia:<br />This occurs as a result of a defect in the genes responsible for producing the alpha chain of hemoglobin.<br /><br />Beta Thalassemia:<br />This occurs as a result of a defect in the genes responsible for producing the beta chain of hemoglobin, and is the most common type.<br /><br />Each type is divided into degrees based on the severity of the disease, including:<br /><br />Thalassemia major: The most severe type, requiring periodic blood transfusions.<br /><br />Thalassemia intermedia: Its symptoms are less severe.<br /><br /> Thalassemia minor: It often causes no obvious symptoms and is discovered incidentally.<br /><br />Symptoms<br />Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the disease, most notably:<br /><br />Chronic anemia.<br /><br />Pallor or yellowing of the skin.<br /><br />Fatigue and general exhaustion.<br /><br />Delayed growth in children.<br /><br />Enlarged liver and spleen.<br /><br />Osteoporosis and facial and skull bone deformities in severe cases.<br /><br />Diagnostic Methods<br />Thalassemia is diagnosed through:<br /><br />Complete blood count (CBC).<br /><br />Special hemoglobin tests, such as hemoglobin electrophoresis.<br /><br />Genetic testing to determine the type of gene mutation.<br /><br />Premarital screening to detect carriers.<br /><br />Treatment<br />There is no definitive cure for all cases, but the disease can be managed through:<br /><br />Regular blood transfusions to maintain normal hemoglobin levels.<br /><br />Iron chelation therapy to prevent iron buildup resulting from repeated blood transfusions.<br /><br />Folic acid to improve blood cell production. <br /><br />Bone marrow transplantation is the only potential cure, but it requires a genetic match with the donor.<br /><br />Gene therapy is a newer method under research and development.<br /><br />Prevention<br />The best methods for preventing thalassemia are:<br /><br />Premarital genetic testing.<br /><br />Genetic counseling for families with a history of the disease.<br /><br />Community awareness about the disease and its spread.<br /><br />Conclusion<br />Thalassemia is a chronic disease that requires ongoing medical care. However, medical advances and modern technologies have helped improve the lives of patients.<br /><br /><br />Al-Mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq.