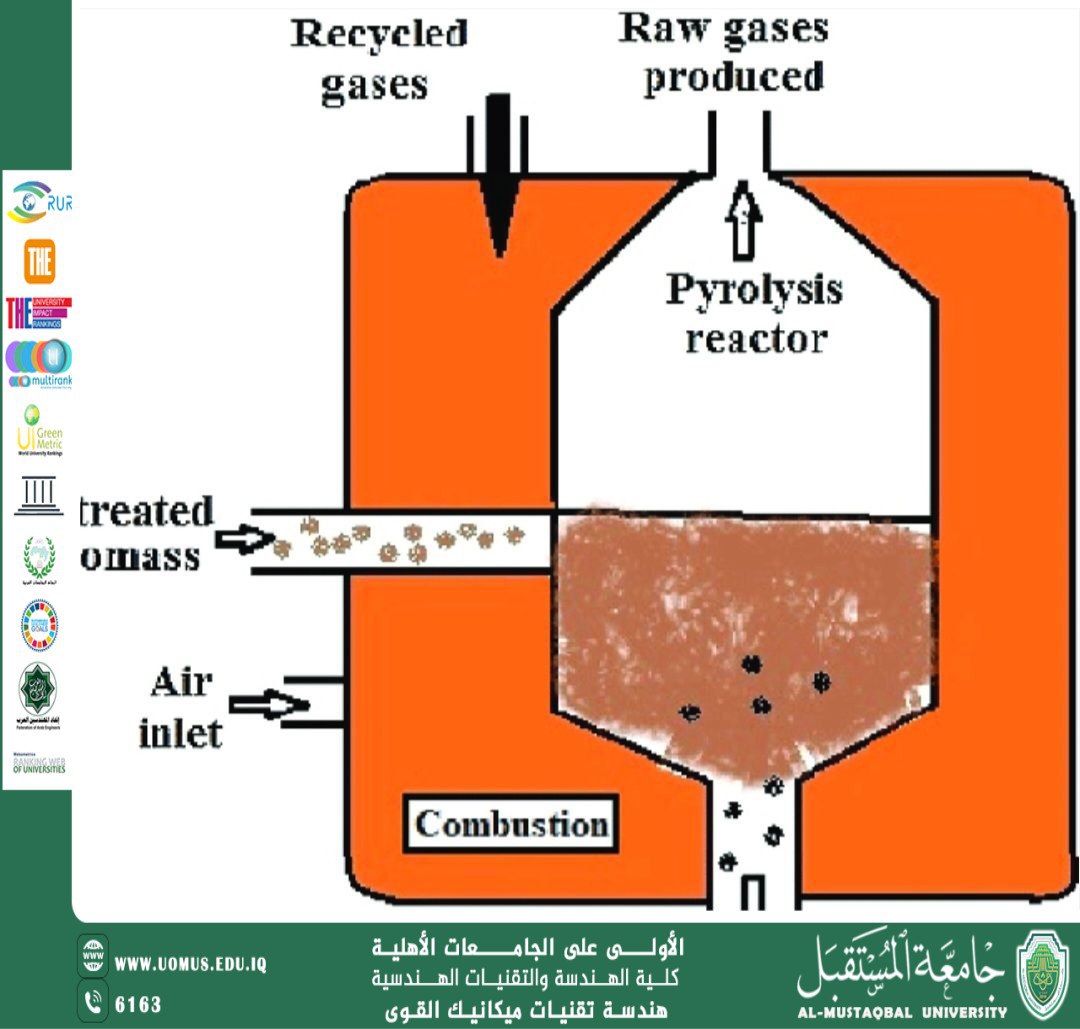
Pyrolysis: An Overview
<br />Definition:<br />Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition process of organic materials at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen. The word "pyrolysis" comes from the Greek words pyro (fire) and lysis (separating), indicating the breaking down of materials by heat.<br /> How Pyrolysis Works<br /><br />In a pyrolysis system, biomass or other organic waste is heated in an oxygen-free environment. Unlike combustion or gasification, pyrolysis doesn’t burn the material but instead breaks it down into three primary products:<br /><br />1. Biochar (solid) – A carbon-rich solid used for soil improvement or as a carbon sequestration method.<br />2. Bio-oil (liquid) – A dark brown combustible liquid that can be refined into fuel.<br />3. Syngas (gas) – A mixture of gases such as hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide, which can be used for energy.<br /><br /> Feedstocks for Pyrolysis<br /><br />Pyrolysis can process a wide variety of organic materials, such as:<br /><br />Agricultural residues (e.g., corn stalks, rice husks)<br /><br />Forestry waste (e.g., wood chips, sawdust)<br /><br />Municipal solid waste (e.g., plastics, paper)<br /><br />Sewage sludge<br /><br />Waste tires<br /><br /> Applications of Pyrolysis<br /><br />Energy production: Pyrolysis products can be used to generate heat, electricity, or refined fuels.<br /><br />Waste management: Reduces the volume of waste and converts it into useful byproducts.<br /><br />Soil enhancement: Biochar improves soil fertility and retains water.<br /><br />Carbon sequestration: Biochar can store carbon for centuries, helping mitigate climate changes <br /><br />Advantages of Pyrolysis<br /><br />Converts waste into valuable products<br /><br />Reduces landfill usage<br /><br />Produces renewable energy<br /><br />Can operate on a wide variety of feedstocks<br /><br />Helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions<br />Disadvantages of Pyrolysis<br /><br />High initial setup cost<br /><br />Requires careful control of temperature and feedstock<br /><br />Bio-oil may require further refining before use<br /><br />Emissions control is necessary to prevent environmental impact<br /><br /> Types of Pyrolysis<br /><br />1. Slow Pyrolysis – Long residence time and low heating rate; optimized for biochar production.<br />2. Fast Pyrolysis – Short residence time and high heating rate; maximizes bio-oil yield.<br />3. Flash Pyrolysis – Extremely fast heating and short vapor residence time; produces mainly vapors and gases.<br /> Conclusion<br />Pyrolysis is a promising technology for sustainable waste management and renewable energy production. As interest in green technologies grows, pyrolysis offers a flexible solution to convert waste into valuable resources while reducing environmental impact.<br /><br />M.Sc Abrar Abdulkareem <br />AlMustaqbal university the first university in Iraq