A scientific article by the teaching assistant (Iftikhar Thamer) entitled "Fields of Medical Physics"
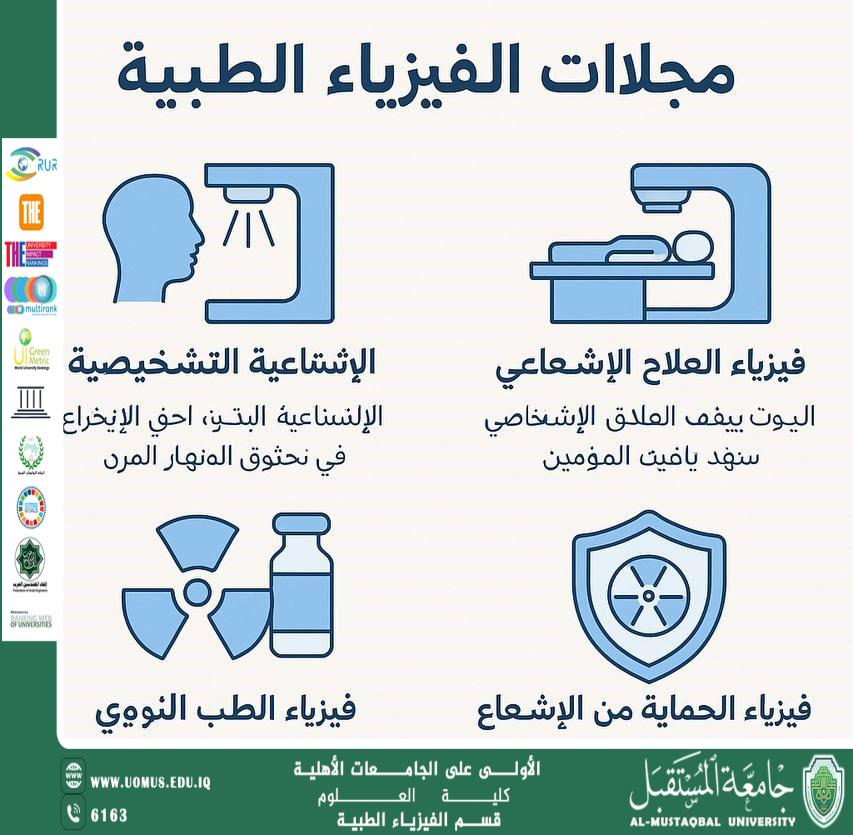
Introduction<br />Medical physics is a branch of applied physics that focuses on the application of physical principles and techniques in medicine and healthcare. Medical physicists play a vital role in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention by developing and managing medical technologies and ensuring radiation safety for both patients and healthcare professionals.<br /><br /><br />1. Diagnostic Radiological Physics<br /><br />This field involves the use of X-rays, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and other electromagnetic waves to visualize internal body structures for diagnosis. Medical physicists in this area work on:<br /> • Improving medical image quality.<br /> • Reducing radiation dose to patients.<br /> • Regular calibration and maintenance of imaging devices.<br /> • Ensuring proper function of equipment such as CT scanners and MRI systems.<br /><br /><br />2. Radiation Therapy Physics<br /><br />Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation, like gamma rays or electrons, to treat cancer and other diseases. Medical physicists in this field are responsible for:<br /> • Accurate dose planning using specialized software.<br /> • Ensuring the tumor receives the correct dose while protecting healthy tissues.<br /> • Calibrating machines such as linear accelerators.<br /> • Conducting quality assurance and safety checks in radiation treatment procedures.<br /><br /><br />3. Nuclear Medicine Physics<br /><br />This field involves the use of radioactive isotopes for diagnosis and treatment. It includes:<br /> • Imaging internal organs using gamma cameras.<br /> • Measuring the distribution of radioactive materials within the body.<br /> • Calculating radiation doses for patients and staff.<br /> • Supporting advanced techniques like PET and SPECT scans.<br /><br /><br />4. Radiation Protection Physics<br /><br />Radiation protection focuses on minimizing the harmful effects of radiation on patients, staff, and the environment. Responsibilities include:<br /> • Designing shielding and radiation-safe facilities.<br /> • Implementing safety protocols in imaging and therapy departments.<br /> • Monitoring radiation doses with precise instruments.<br /> • Training healthcare teams on safe handling of radiation sources.<br /><br />5. MRI Physics<br /><br />A sub-specialty focused on magnetic resonance imaging used for soft tissue visualization. Medical physicists working with MRI:<br /> • Calibrate systems and optimize image quality.<br /> • Enhance technical parameters for clearer imaging.<br /> • Address patient safety concerns related to strong magnetic fields.<br /><br />6. Medical Instrumentation Physics<br /><br />This area focuses on the design, operation, and maintenance of various medical devices, including:<br /> • Heart and blood pressure monitors.<br /> • Mechanical ventilators.<br /> • Laser surgical tools.<br /> • Systems for measuring bioelectrical signals like ECG, EEG, and EMG.<br /><br />Conclusion<br /><br />Medical physics is a diverse and evolving field that blends science and technology to enhance human health. Its significance is growing with the advancement of medical technologies. As innovations like artificial intelligence, 3D imaging, and targeted therapies emerge, the role of medical physicists will expand, making them essential in the future of healthcare.<br /><br /><br /><br />"AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq"<br/><br/><a href=https://uomus.edu.iq/Default.aspx target=_blank>al-mustaqbal University Website</a>