The Impact of Wind Speed and Direction on Wind Turbine Efficiency
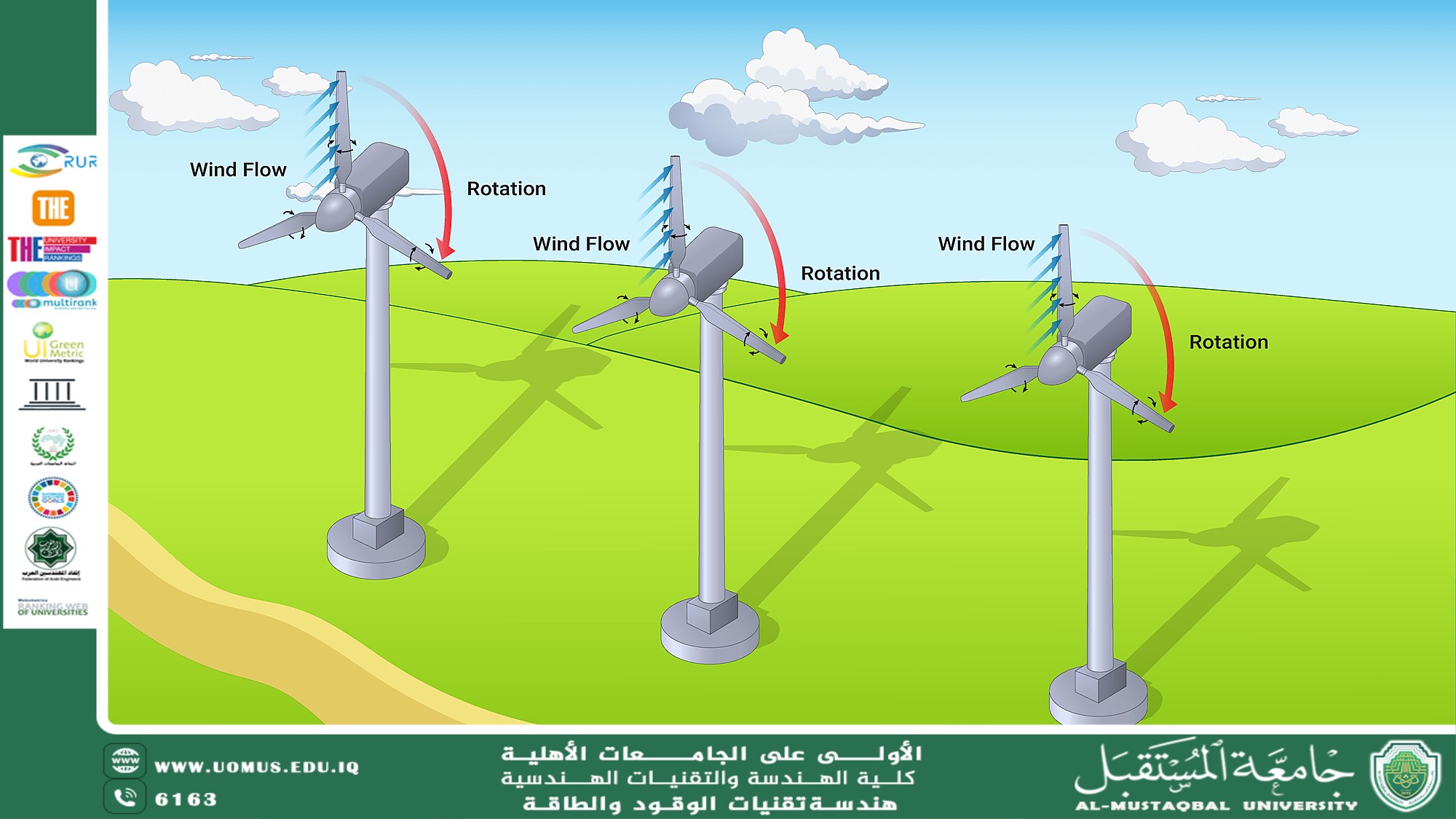
The Impact of Wind Speed and Direction on Wind Turbine Efficiency<br />Eng. Nourhan Thamer Assi<br /><br />Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)<br />This topic contributes directly to:<br />Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy – Enhancing the reliability and output of wind energy systems.<br />Goal 13: Climate Action – Promoting clean energy to combat climate change.<br />Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure – Supporting the development of smarter, more adaptive wind technologies.<br /><br />Introduction<br />Wind turbines rely on the natural movement of air to generate electricity. However, not all wind conditions are equally beneficial. Wind speed and direction are two critical factors that influence the efficiency and performance of wind turbines. Understanding and adapting to these variables is essential for maximizing power output and ensuring long-term reliability of wind energy systems.<br /><br />1. The Role of Wind Speed in Energy Generation<br />Wind turbines are designed to operate efficiently within a specific range of wind speeds, typically between 3 m/s (cut-in speed) and 25 m/s (cut-out speed).<br />At low wind speeds, the turbine produces little to no electricity.<br />Between optimal speeds (often 12–15 m/s), the turbine reaches peak efficiency.<br />At very high speeds, turbines automatically shut down to prevent mechanical damage.<br />Power Output Relation:<br />Wind power output increases with the cube of wind speed (P ∝ V³), meaning even small increases in wind speed can lead to significant increases in energy production.<br /><br />2. Importance of Wind Direction<br />Wind turbines are most efficient when facing directly into the wind. Deviations in wind direction affect:<br />Angle of attack on turbine blades.<br />Yaw control system performance (which aligns the turbine with the wind).<br />Wake effects in wind farms, where turbines downwind receive less energy due to upstream interference.<br />Poor alignment reduces aerodynamic efficiency and can lead to mechanical strain on the yaw system and blade components.<br /><br />3. Measuring and Responding to Wind Conditions<br />To operate efficiently, turbines rely on advanced systems that monitor and respond to changing wind conditions:<br />Anemometers and wind vanes measure speed and direction in real-time.<br />Yaw motors rotate the nacelle to align with wind direction.<br />Blade pitch control adjusts the angle of blades to optimize lift and reduce stress.<br />LIDAR systems (Light Detection and Ranging) can detect wind conditions ahead of the turbine for proactive adjustments.<br /><br />4. Turbulence and Wind Shear<br />Other wind characteristics also affect turbine performance:<br />Turbulence (sudden, irregular changes in wind) reduces efficiency and increases wear.<br />Wind shear (variation of wind speed with height) can cause uneven loading on the blades.<br />These effects are especially important in complex terrain or urban environments, requiring customized turbine designs and placement strategies.<br /><br />5. Optimizing Turbine Placement and Design<br />To maximize the impact of wind speed and direction, engineers:<br />Conduct wind resource assessments before building wind farms.<br />Use computational models to predict wind behavior over time.<br />Design turbines with adaptive controls that optimize performance under variable wind conditions.<br />Strategically space turbines to reduce wake interference in large arrays.<br /><br />Conclusion<br />Wind speed and direction are not just environmental factors—they are core design and operational parameters that determine the success of wind energy systems. By understanding and adapting to these variables through smart technology and careful planning, we can ensure that wind turbines operate at peak efficiency, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.<br /><br />Al-Mustaqbal University – The No. 1 Private University in Iraq<br />