A scientific article by Assistant Lecturer Mohaimen Sameer Aref titled ( The Role of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Early Detection of Glaucoma)
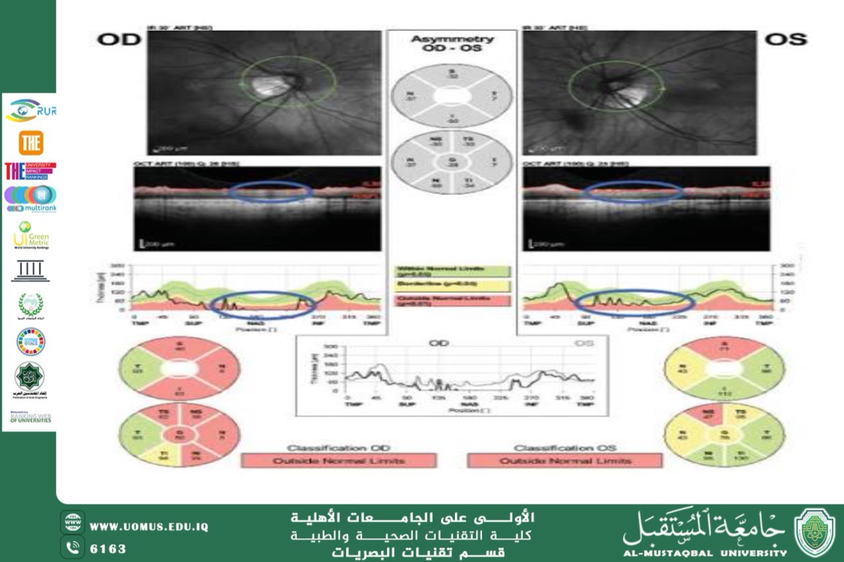
Glaucoma is a leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. Early detection is crucial to prevent progression. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has emerged as a non-invasive imaging technique capable of capturing high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina and optic nerve head. This article reviews the clinical significance of OCT in detecting early glaucomatous changes, particularly in the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and ganglion cell complex (GCC).<br /><br />Glaucoma often remains asymptomatic in early stages, making routine screening essential. Traditional methods such as visual field testing may fail to detect pre-perimetric glaucoma. OCT provides quantitative structural data that precedes functional loss, giving clinicians a head start in initiating treatment.<br /><br />OCT scans were analyzed in patients suspected of glaucoma and compared with control subjects. Measurements of RNFL thickness, optic cup/disc ratio, and GCC integrity were used as primary indicators. Follow-ups were conducted over a 12-month period to monitor structural changes.<br /><br />The study revealed that OCT could detect subtle thinning of RNFL even before visual field changes occurred. A significant correlation was found between RNFL thinning and intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation. The ability of OCT to generate objective, reproducible measurements makes it indispensable for glaucoma management.<br /><br />OCT plays a pivotal role in the early diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma. Its integration into routine optometric and ophthalmologic evaluations can significantly reduce the risk of late-stage vision loss through timely intervention.