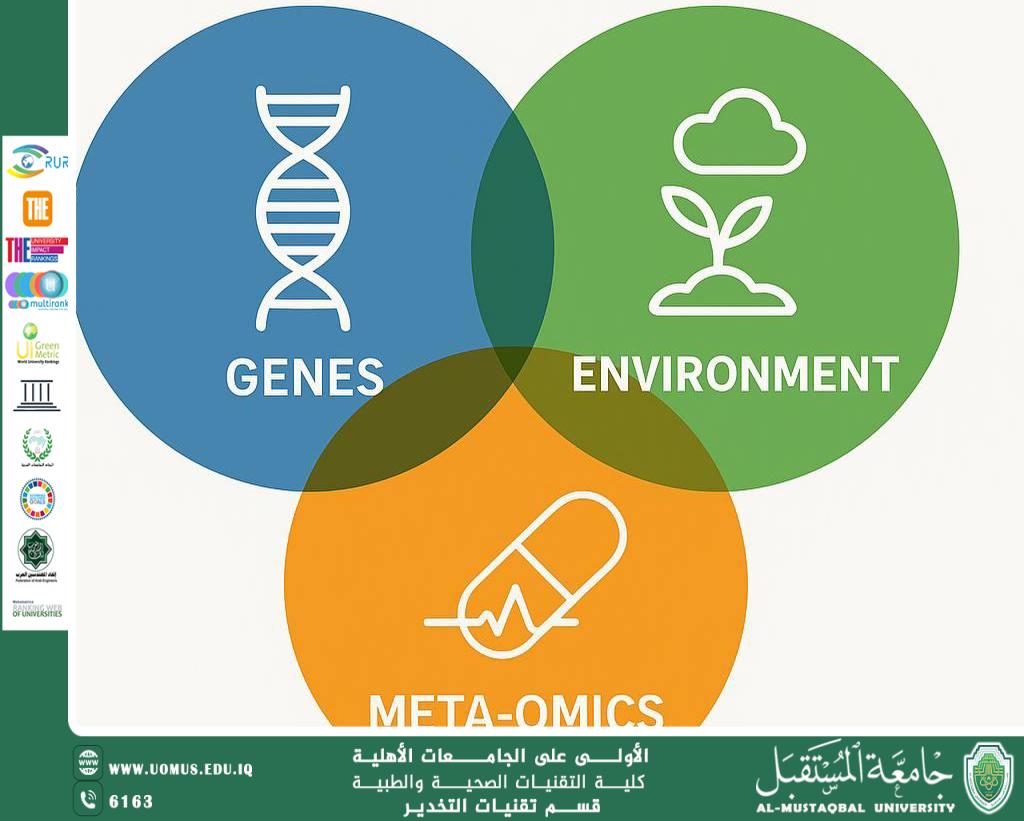
Post-Genomic Medicine: The Interaction Between Genes, Environment, and Meta-Omics
Introduction :<br /><br />In recent decades, medicine has witnessed a tremendous revolution thanks to the Human Genome Project, which unveiled the complete genetic map. However, it soon became clear that knowing gene sequences alone is insufficient to fully understand the biological complexity of diseases. This gave rise to the concept of Post-Genomic Medicine, a field that focuses on understanding the interactive relationship between genes, environmental factors, and other “omics” layers such as the proteome, metabolome, microbiome, and epigenome.<br /><br />The primary goal of this approach is to move beyond a one-dimensional view of disease (genes only) toward a multidimensional perspective, where health and disease emerge from a dynamic network of interactions.<br /><br />The Concept of Meta-Omics<br /><br />“Meta-Omics” is an umbrella term that encompasses several disciplines:<br /> • Metagenomics: The study of the genetic material of all microorganisms in a given environment, such as the gut.<br /> • Metabolomics: The analysis of all metabolites present in cells or body fluids.<br /> • Microbiome: The full composition of microbial communities inhabiting the human body.<br /> • Epigenome: Chemical modifications on DNA or associated proteins that regulate gene activity without altering the sequence itself.<br /><br />These layers provide complementary data to the genome and reveal how internal and external environments interact with inherited genetics.<br /><br />Gene–Environment Interaction<br /><br />Chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer often do not result from a single “faulty gene,” but rather from a complex network influenced by:<br /> • Environmental factors: diet, physical activity, pollutants, sleep patterns, stress.<br /> • Molecular changes: in the metabolome and microbiome.<br /> • Genetic susceptibility: inherited predisposition interacting with external conditions.<br /><br />Example: Two individuals carrying the same diabetes-associated mutation may have different outcomes: one may develop the disease due to an unhealthy diet, while the other may avoid it through a balanced lifestyle.<br /><br />Clinical Applications :<br /><br /> 1. Early Diagnosis<br /> • Liquid biopsies that detect early molecular signatures of cancer.<br /> • Biomarkers from the metabolome or microbiome to predict chronic disease risk.<br /> 2. Personalized Therapy<br /> • Designing treatment plans based on the patient’s genes, gut microbiome composition, and biochemical responses.<br /> • Adjusting drug dosages according to omics profiles to minimize side effects.<br /> 3. Preventive Medicine<br /> • Linking environmental data (exposome) with meta-omics to identify individual risk factors.<br /> • Building Dynamic Risk Scores to guide preventive interventions.<br /><br />Challenges :<br /><br /> • Data complexity and volume: Require advanced analytical tools in AI and machine learning.<br /> • Privacy and ethics: Collecting omics and environmental data demands strict data protection.<br /> • Research inequality: Most major databases rely heavily on European-origin samples, threatening the fairness of results.<br /><br />Future Perspectives :<br /><br /> • Integrating omics data with electronic health records to facilitate clinical use.<br /> • Nanotechnology and bio-robots for precise delivery of therapies targeting specific molecular pathways.<br /> • Explainable AI to uncover non-linear relationships between genes, environment, and meta-omics.<br /><br />Conclusion :<br /><br />Post-genomic medicine represents a paradigm shift in healthcare, combining genetic, environmental, and meta-omics sciences to provide a holistic vision of human health. With continued advances in analytical tools and more equitable representation in research, this field is expected to become the cornerstone of Precision Medicine in the coming decades.<br /><br />Zahraa Jawad Sabr<br /><br />Al-Mustaqbal University <br />The First University in Iraq.