Article Title: "Computed Tomography (CT): A Revolution in Detecting Tumors and Cardiac Diseases" By: Lecturer Mustafa Khalil Hassan
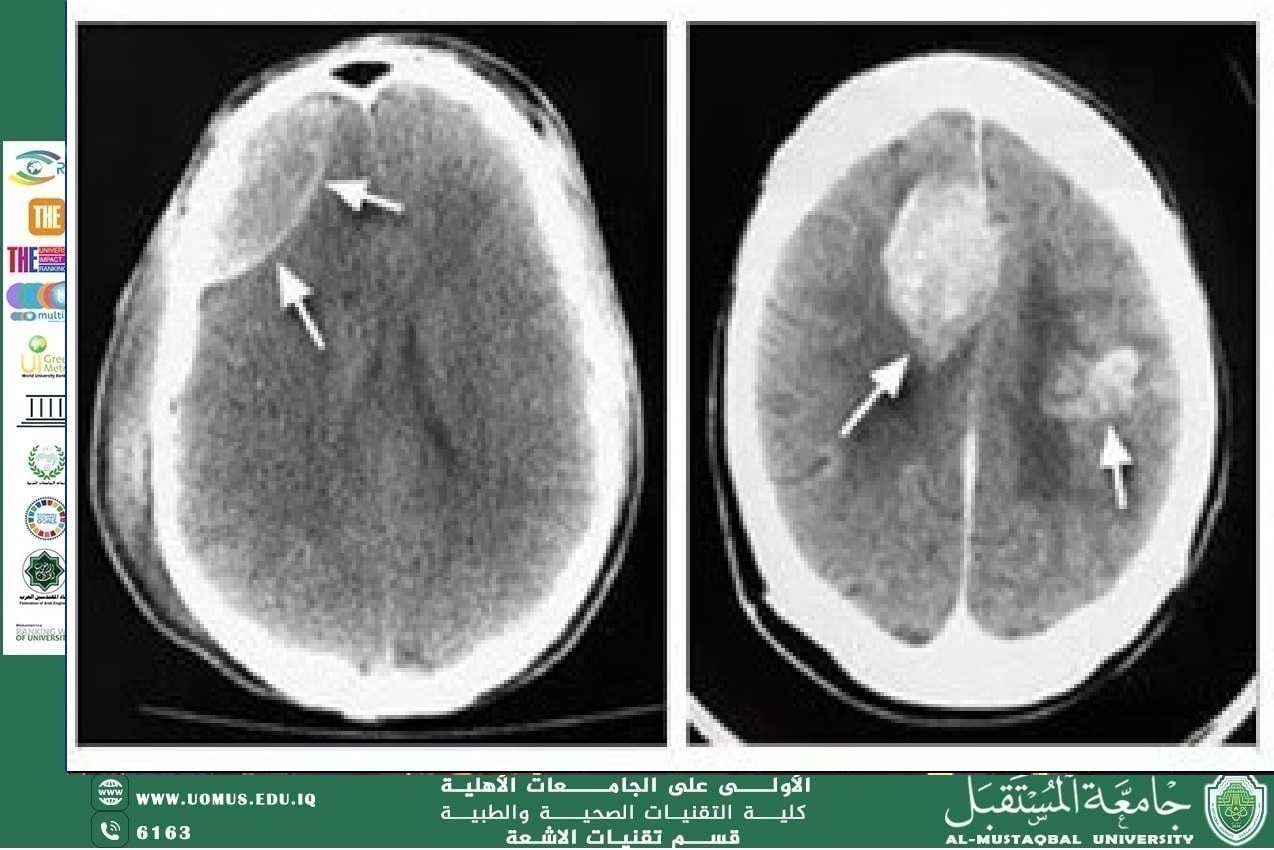
Article Title: "Computed Tomography (CT): A Revolution in Detecting Tumors and Cardiac Diseases"<br />By: Lecturer Mustafa Khalil Hassan<br /><br />Introduction<br />Since the emergence of medical imaging technologies, Computed Tomography (CT-Scan) has represented a major breakthrough in disease diagnosis. It relies on X-rays combined with computer processing to produce precise three-dimensional cross-sectional images of the body. Today, it has become one of the essential tools for detecting tumors and cardiac diseases, assisting physicians in early diagnosis and enabling effective treatment planning.<br /><br />Principle of CT Imaging<br />The CT scanner works by rotating an X-ray tube around the patient, emitting hundreds of X-rays from different angles. A computer then processes this data to generate accurate cross-sectional images, which can later be reconstructed into a three-dimensional model of the organs.<br /><br />Role of CT in Tumor Detection<br /><br />Early Diagnosis: Enables detection of tumors even at their earliest stages.<br /><br />Localization and Size Determination: Assists surgeons in planning precise surgical interventions.<br /><br />Monitoring Treatment Response: Such as evaluating tumor size after chemotherapy or radiotherapy.<br /><br />Tumor Differentiation: Helps distinguish between benign and malignant tumors when combined with other techniques such as PET-CT.<br /><br />Role of CT in Diagnosing Cardiac Diseases<br /><br />Detection of Coronary Artery Stenosis: Through imaging of the arteries using contrast dye.<br /><br />Diagnosis of Cardiac Thrombosis: Enables rapid and accurate detection of arterial blockages.<br /><br />Assessment of the Heart Muscle: Demonstrates the extent of damage after heart attacks.<br /><br />3D Cardiac Imaging: Provides physicians with precise visualization of the heart’s internal structures and vessels.<br /><br />Advantages<br /><br />High speed in conducting examinations.<br /><br />Extremely detailed accuracy compared to traditional X-rays.<br /><br />Ability to produce three-dimensional images of organs.<br /><br />Vital tool in emergency departments for detecting bleeding or clots.<br /><br />Challenges and Risks<br /><br />Radiation Exposure: The dose is higher than that of conventional X-rays.<br /><br />Contrast Material Sensitivity: Some patients may experience allergic reactions.<br /><br />High Cost: Both devices and examinations are expensive.<br /><br />Conclusion<br />Computed Tomography (CT) is a true revolution in the field of medical diagnostics, significantly contributing to saving thousands of lives through the early detection of tumors and cardiac diseases. With continuous advancements in modern technologies such as Low-dose CT and integration with Artificial Intelligence, this approach is expected to become even safer and more accurate in the coming years.<br /><br />Al-Mustaqbal University – The First University in Iraq