مقاله Mobility with Bionic Limbs"للأستاذ ماهر عبد الأمير رحمن
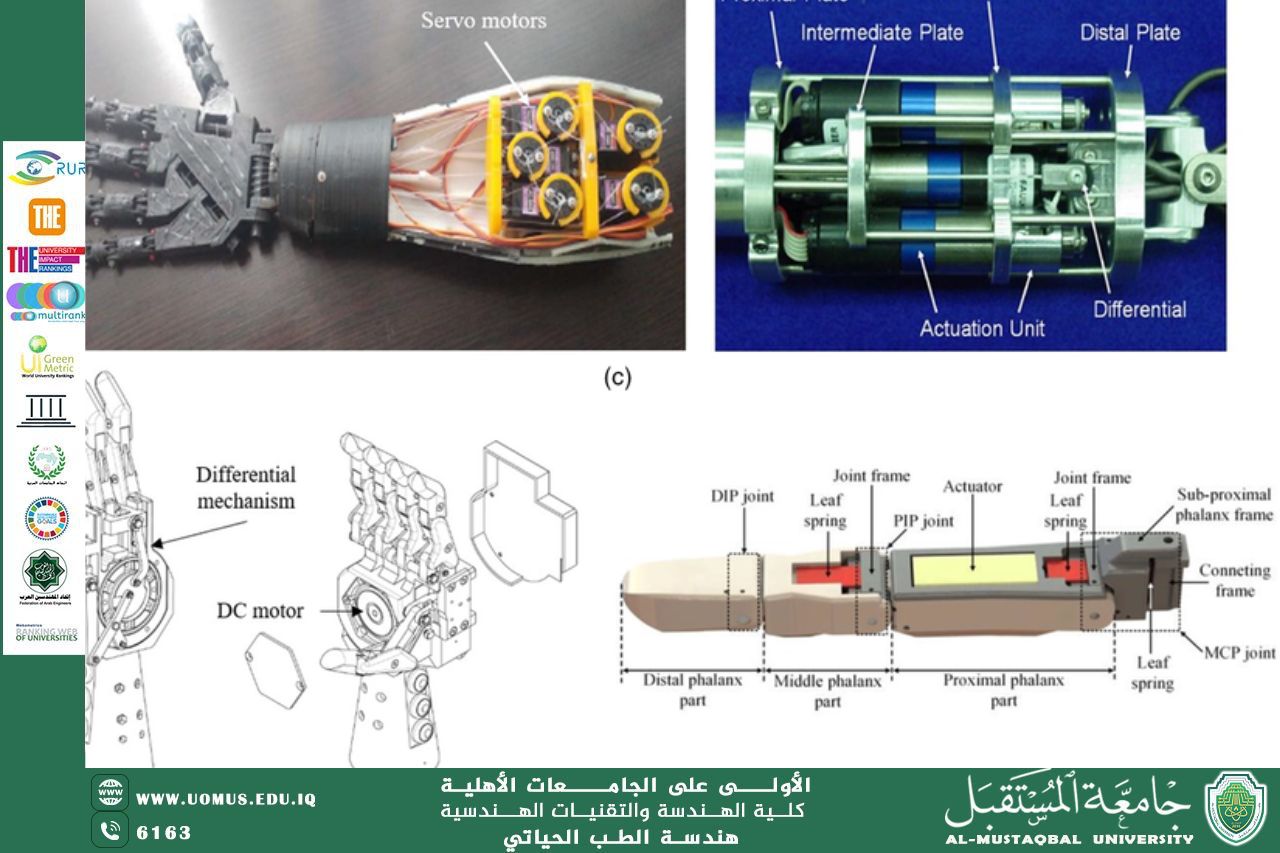
Recent advancements in prosthetics, especially bionic limbs, have significantly improved the lives of individuals with limb loss. These prosthetic devices are designed to restore functional mobility by using advanced technologies such as myoelectric control, where the device reads electrical signals from the user's muscles, and neural interfaces, which allow for direct brain control.
The integration of sensors and actuators enables the prosthesis to perform complex movements, mimicking natural limb function. These prosthetics offer enhanced dexterity, from the ability to grasp delicate objects to complex tasks like walking on uneven terrain. Additionally, with the help of machine learning algorithms, bionic limbs can learn and adapt to a user's movements over time, improving their responsiveness and overall user experience. Researchers are working on improving the sensory feedback from these devices, making them feel more natural for users.
Some bionic limbs now feature advanced touch sensors, which allow users to experience sensations of pressure or texture. This innovation could significantly impact not only limb amputees but also those with various neurological conditions. As the technology progresses, bionic limbs are becoming increasingly affordable and accessible, offering people greater independence and quality of life