Modern Techniques in Diagnosing Microbial Infections
Modern Techniques in Diagnosing Microbial Infections
Introduction
Diagnosing microbial infections has become more accurate and faster due to continuous advancements in biological and molecular technologies. Accurate identification of the causative microorganism is essential for selecting the appropriate treatment and limiting the spread of diseases. Modern diagnostic tools now go beyond traditional culture and microscopy methods, allowing results to be obtained within hours instead of days.
1. Molecular Diagnosis Based on DNA Analysis
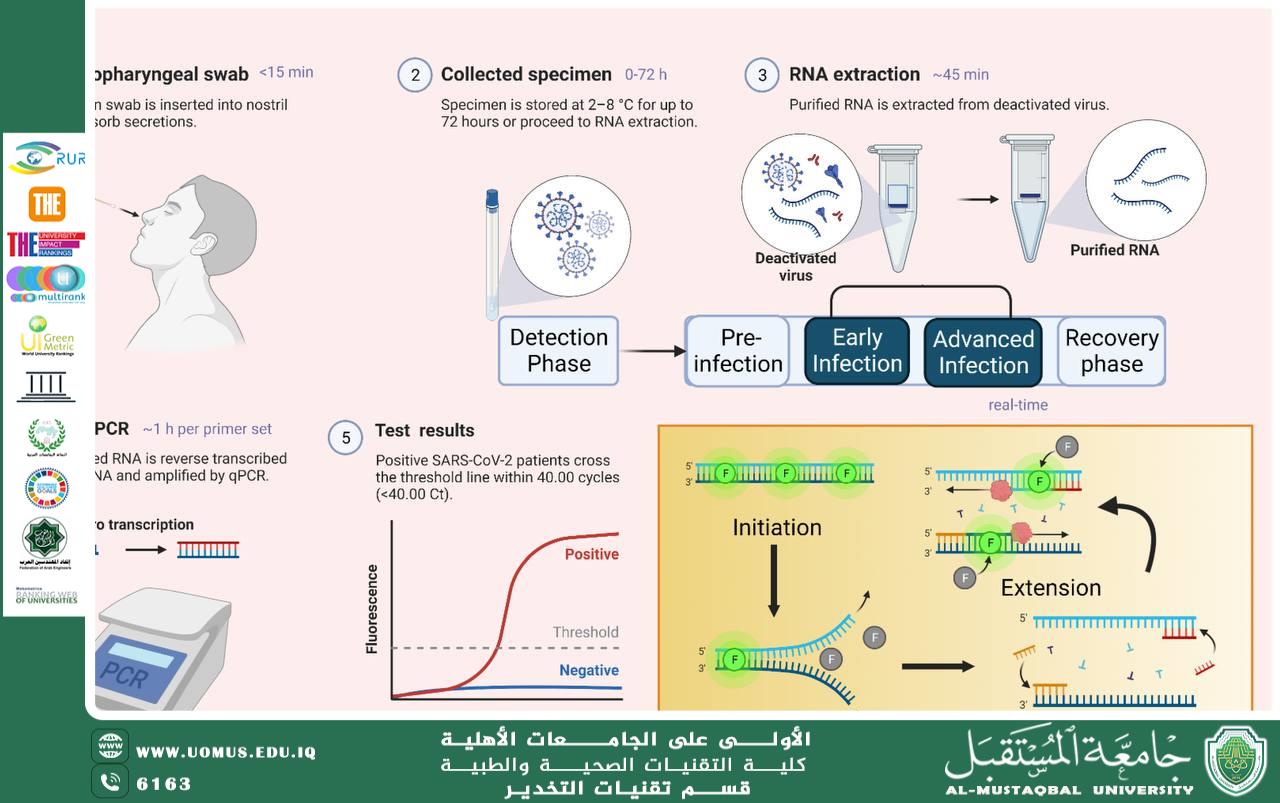
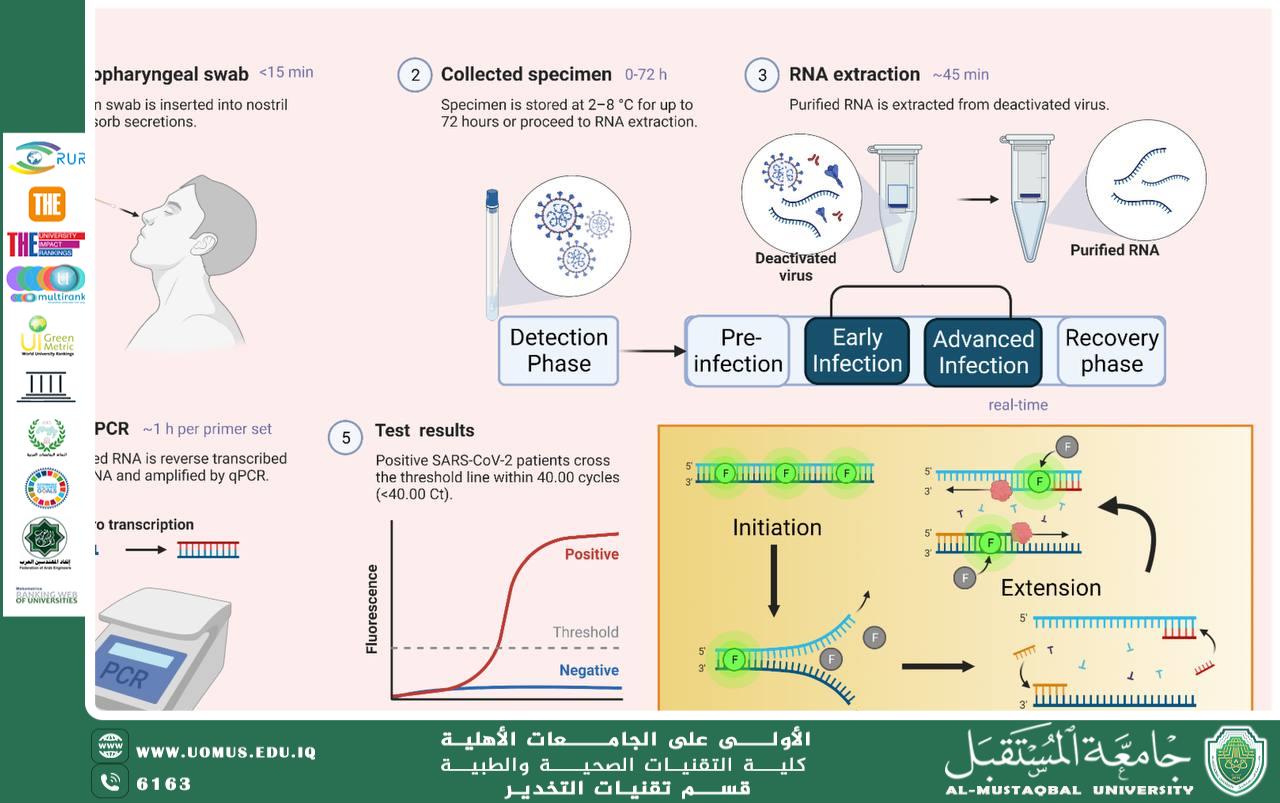
1. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):
A highly sensitive technique used to detect microbial genetic material, enabling rapid identification of viruses and bacteria even at very low concentrations.
2. RT-PCR:
Used to detect RNA viruses such as influenza viruses and coronavirus, offering high sensitivity and specificity.
3. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS):
Provides comprehensive analysis of microbial genomes, allowing detection of known and emerging pathogens, along with genetic mutations and drug resistance markers.
2. Rapid Protein-Based Diagnostic Techniques
1. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry:
Identifies bacteria and fungi within minutes by analyzing their protein profiles, significantly reducing diagnostic time.
2. Antigen Tests:
Widely used for rapid detection of certain viruses and bacteria, with the advantage of simplicity and immediate results.
3. Immunological Diagnostic Techniques
1. ELISA Tests:
Based on antigen–antibody interactions, useful for detecting current or past infections.
2. Rapid Immunoassays: Applied in emergency settings for preliminary detection of viruses such as HIV and hepatitis.
4. Enhanced Culture Techniques and Automated Systems
1. Automated Culture Systems:
Accelerate bacterial detection through continuous monitoring of chemical changes in culture media.
2. Automated Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing:
Provides timely identification of effective antibiotics compared to traditional manual methods.
5. Diagnosis Using Artificial Intelligence
Modern systems incorporate artificial intelligence to analyze microbial data, recognize infection patterns, and predict causative agents. AI is also used in automated analysis of culture images and microscopic slides.
Conclusion
Modern diagnostic technologies have revolutionized the detection of microbial infections, improving accuracy, reducing diagnostic time, and supporting optimal treatment selection. Continued development in these technologies strengthens health systems’ capabilities in combating infectious diseases and enhancing epidemiological surveillance.
Zainab Mohammed Jawad
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq.