Immunity and Infectious Diseases — How the Body Defends Itself Against Invaders
ntroduction
The human body possesses an extraordinary defense system known as the immune system, which protects it from viruses, bacteria, and parasites. The immune cells work in a precisely coordinated manner, much like an organized army, identifying invaders, attacking them, and remembering them to prevent future infections.
What Is the Immune System?
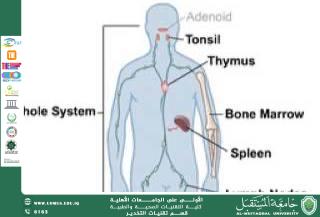
The immune system is made up of organs, cells, and molecules that work together to protect the body. These include:
• White blood cells (lymphocytes, phagocytes, and natural killer cells).
• Lymphoid organs such as the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow.
• Antibodies that bind to pathogens and neutralize them.
Types of Immunity
1. Innate (Natural) Immunity
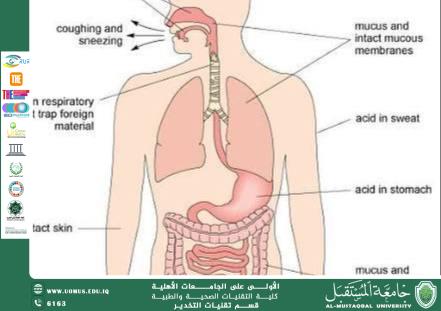
• The first line of defense against any foreign substance.
• Rapid and non-specific.
• Includes the skin, mucous membranes, and inflammation.
2. Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity
• Develops after exposure to a disease or a vaccine.
• Depends on B and T lymphocytes.
• Characterized by its memory and rapid response to repeated infections.
How Infection Occurs
When a pathogen (virus or bacterium) enters the body:
1. Immune cells recognize it.
2. Inflammation begins as a defensive response.
3. Antibodies are produced to eliminate the pathogen.
4. Immune memory forms to prevent future infection by the same agent.
Common Infectious Diseases
• Influenza: Caused by a constantly mutating virus.
• Tuberculosis (TB): Airborne disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• COVID-19: A major pandemic of the modern era.
• Viral Hepatitis (A, B, C): Infects the liver with varying transmission routes.
• HIV/AIDS: A virus that attacks the immune system itself.
Vaccines: The Smart Weapon of Immunity
A vaccine introduces a weakened or inactive form of a pathogen to the immune system, prompting an immune response without causing disease.
Vaccines are among the greatest achievements in medicine, saving millions of lives from deadly diseases such as polio and measles.
Weakening of the Immune System
The immune system may become weakened due to:
• Poor nutrition or vitamin deficiencies.
• Chronic stress and fatigue.
• Chronic diseases such as diabetes or cancer.
• Immunosuppressive medications.
As a result, the body becomes more vulnerable to recurrent infections.
Natural Ways to Strengthen Immunity
1. Ensure adequate and restful sleep.
2. Eat foods rich in vitamins C, D, and zinc.
3. Exercise regularly.
4. Avoid smoking and alcohol.
5. Reduce chronic psychological stress.
Conclusion
Immunity is not merely a defensive wall but a smart, adaptive network that learns, remembers, and protects. With advances in medicine and vaccination, understanding the immune system has become the key to preventing infectious diseases and maintaining overall health.
Zahraa Jawad
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq