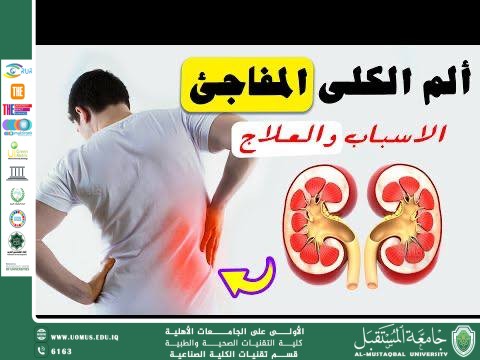
A Scientific Article by Ms. Tabarak Ahmed Turki Al-Azzawi “Sudden Kidney Pain: Causes and Treatment Methods”
Introduction
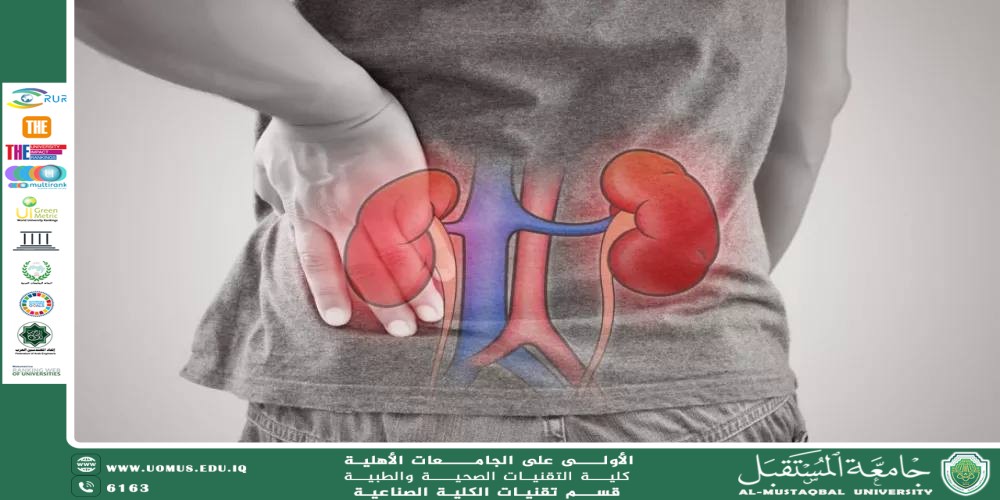
Sudden kidney pain is considered a medical emergency that requires prompt evaluation to identify the underlying cause and determine the appropriate treatment. The causes of this pain vary and may include inflammatory conditions, obstructions, injuries, and other disorders that affect the kidneys and the urinary system.
Causes of Sudden Kidney Pain
1. Kidney Stones
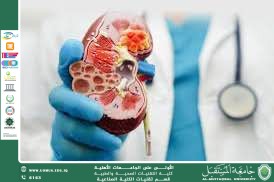
Kidney stones are the most common cause of sudden kidney pain. They occur due to the accumulation of salts and minerals inside the kidneys, leading to obstruction of the urinary tract. This obstruction increases pressure within the kidney, resulting in sharp, intermittent pain.
2. Kidney Infections (Pyelonephritis)
These infections occur due to bacterial invasion of kidney tissues, causing severe pain accompanied by symptoms such as fever, chills, and nausea. The pain is usually constant and worsens as the infection progresses.
3. Kidney Injuries
Trauma or direct impact to the back or abdomen can cause tears or internal bleeding in the kidney tissues, leading to sudden, intense pain.
4. Kidney Cysts or Vascular Disorders
The presence of kidney cysts or vascular obstructions—such as renal vein thrombosis—may cause sudden pain due to pressure or reduced blood flow to the kidney.
Treatment
1. Treatment of Kidney Stones
• Strong pain relievers to manage acute pain
• Antibiotics if there is an associated infection
2. Treatment of Kidney Infections
• Effective antibiotics to treat bacterial infection
• Medical support, including rest and adequate hydration
3. Treatment of Kidney Injuries
• Monitoring and medical support for mild cases
Conclusion
Sudden kidney pain is a symptom with multiple causes that requires accurate diagnosis to identify the underlying condition. Treatment varies depending on the cause, ranging from simple medications to surgical interventions. Early evaluation and prompt treatment help prevent serious complications and improve patients’ quality of life.
Al-Mustaqbal University The First University in Iraq