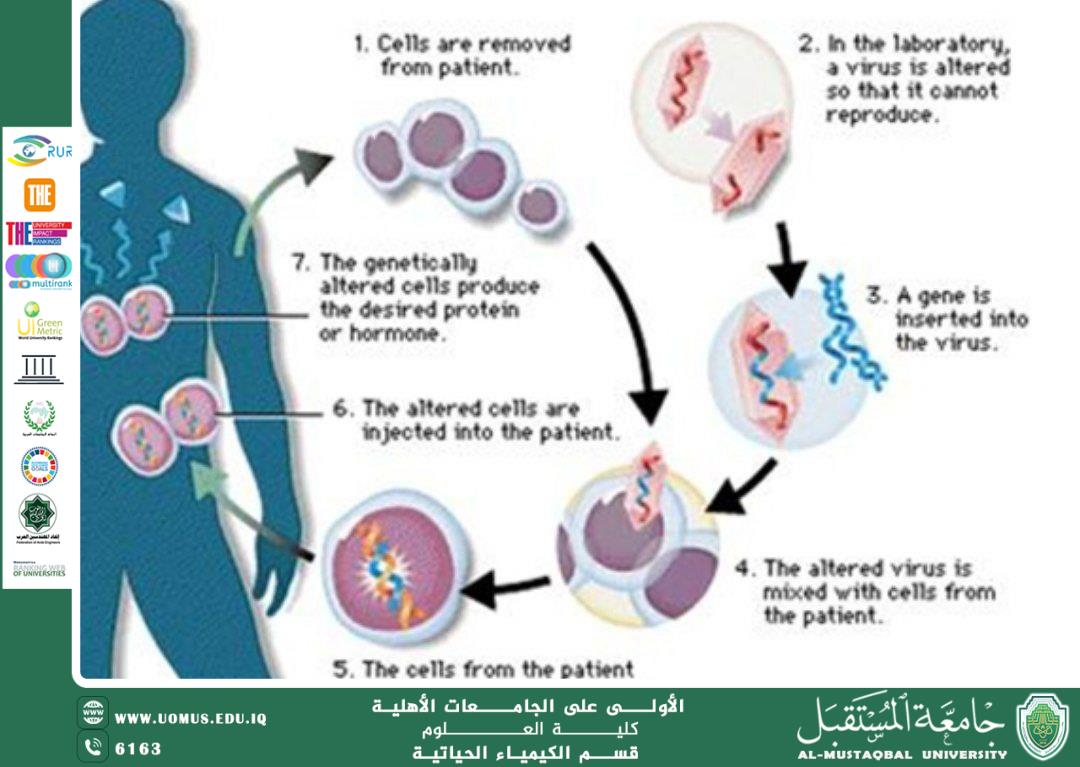
A Scientific Article by Professor Dr. Nasser Abdul Hassan Nasser Title:The Role of Pharmacogenomics in Clinical Laboratory Analysis
Pharmacogenomics is a branch of Personalized Medicine that focuses on how genetic differences between individuals affect their response to drugs. Clinical laboratory analysis, on the other hand, encompasses a set of laboratory tests used to diagnose diseases, monitor treatment, and determine drug interactions.
The integration of pharmacogenomics and clinical laboratory analysis has become a crucial necessity in modern treatment methods, as it enables the determination of optimal dosages, reduces toxicity, and improves drug efficacy by analyzing a patient's genetic makeup.
1. The Concept of Genetic Analysis in Clinical Laboratories
Clinical laboratories are concerned with analyzing:
· Genes responsible for drug metabolism
· Mutations that affect drug response
· Genetic polymorphisms such as SNPs
· Enzymes involved in drug metabolism
· Drug receptors
· Drug Transporters
Techniques used include:
· PCR
· qPCR
· DNA sequencing
· Microarray
· NGS (Next-Generation Sequencing)
2. The Role of Pharmacogenomics in Selecting the Appropriate Drug
Genetic analysis helps determine:
· Which drug will be most effective for the patient
· Which drug may cause toxicity or side effects
· Which drug is ineffective due to a genetic defect
Example:
· Breast cancer patients are tested for the HER2 gene to determine if treatment with Herceptin will be effective.
· CYP2C19 genotype testing before administering Clopidogrel.
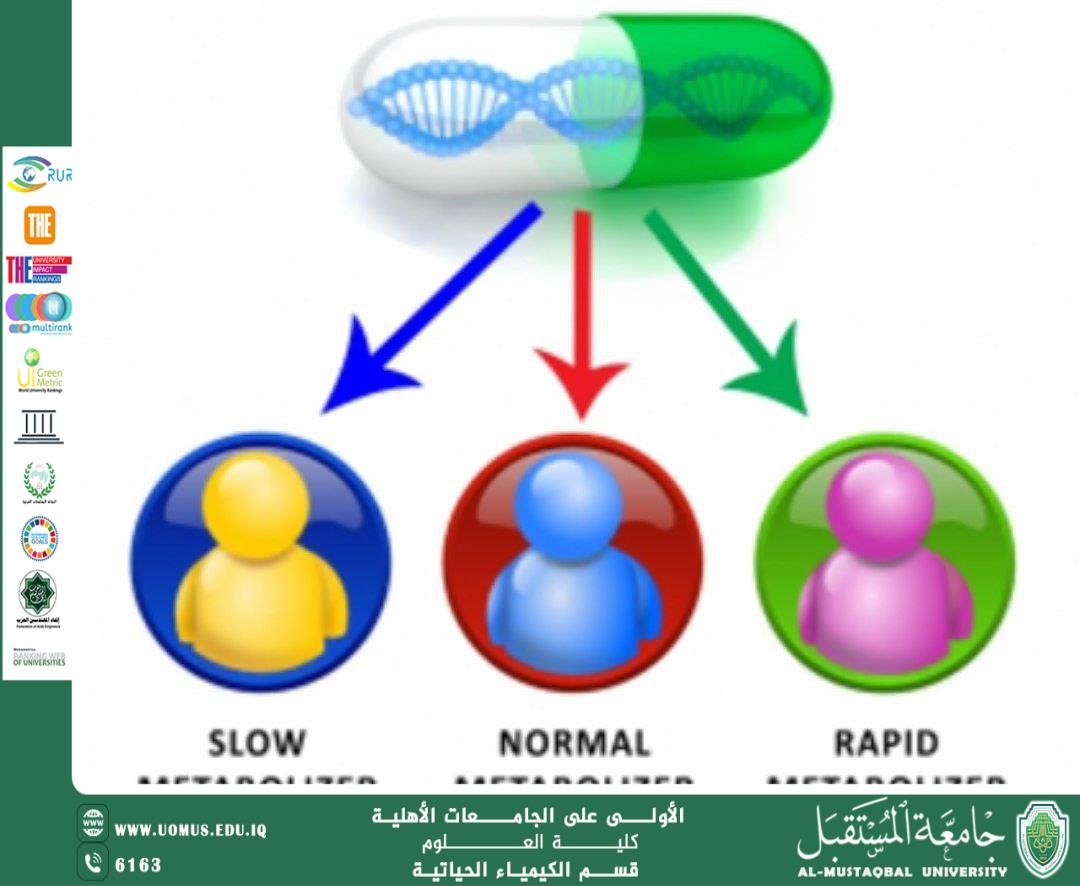
3. The Role of Pharmacogenomics in Determining the Appropriate Dosage (Dose Adjustment)
Genetic variations in metabolic enzymes lead to:
· A patient who metabolizes a drug rapidly → requires a higher dose
· A patient who metabolizes it slowly → requires a lower dose
· Or the drug may be dangerous (Toxic) for them
The most common genes used in clinical laboratories:
· CYP2D6 (antidepressants, analgesics, Tamoxifen)
· CYP2C9 (Warfarin)
· VKORC1 (Warfarin sensitivity)
· TPMT (Thiopurines, cancer drugs)
· UGT1A1 (Irinotecan toxicity)
4. Monitoring Drug Therapy Using Genetic Analysis
Clinical analysis is no longer limited to measuring drug concentration alone; it now includes:
· Identifying mutations that affect the drug's pathway
· Determining the risk of drug toxicity before it occurs
· Monitoring drug response based on the genome
Example:
Testing for HLA-B*1502 before administering Carbamazepine to avoid the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome(SJS).
5. Pharmacogenomics in Clinical Laboratory Analysis for Oncology (Cancer Pharmacogenomics)
It plays a role in:
· Determining immunotherapy
· Selecting chemotherapy
· Determining safe dosages for anticancer drugs
Examples:
· EGFR mutation analysis for treating lung cancer with Gefitinib
· KRAS analysis to assess the effectiveness of Cetuximab
· BRCA1/2 analysis to guide PARP inhibitor therapy
6. Its Role in Clinical Laboratory Analysis for Psychiatric and Neurological Diseases
Genetic analysis helps in:
· Choosing the appropriate antidepressant
· Determining the dosage of antipsychotics
· Reducing serious side effects
Examples:
· CYP2D6 → affects the metabolism of antidepressants
· SLC6A4 → affects the response to SSRIs
· COMT gene → associated with response to certain anti-anxiety medications
7. Improving Patient Safety and Reducing Toxicity
Pharmacogenomics helps in:
· Preventing serious drug interactions
· Detecting patients with high drug sensitivity
· Reducing treatment costs by identifying suitable options from the start
Example:
Analysis of the DPYD gene before administering 5-Fluorouracil to avoid fatal toxicity.
Conclusion
Integrating pharmacogenomics into clinical laboratory analysis is a fundamental step towards modern personalized medicine. It helps in:
· Selecting the correct drug
· Determining the optimal dosage
· Reducing toxicity
· Improving treatment efficacy
· Avoiding medication errors
· Improving treatment outcomes at both the individual and societal levels
As genetic analysis technologies advance, clinical laboratories will play an even greater role in guiding treatment decisions based on the genome.
Al-Mustaqbal University - Ranked 1st Among Iraqi Private Universities