Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosing Heart Diseases — From ECG Analysis to Predicting Cardiac Events
Introduction
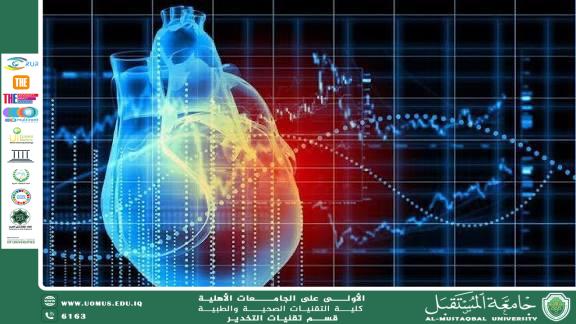
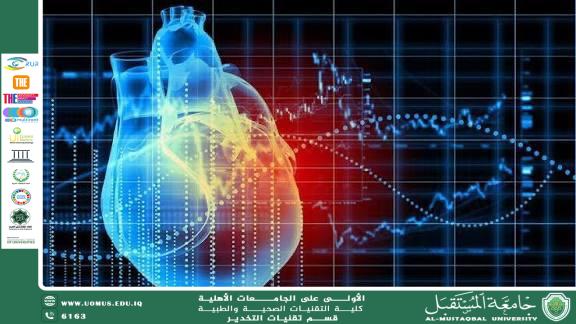
In recent years, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine—especially in cardiology—has witnessed a remarkable transformation. AI algorithms can now analyze massive datasets from electrocardiograms and medical imaging with accuracy that in some cases surpasses human capabilities. These technologies represent a major shift toward early diagnosis and prevention of heart attacks and strokes.
What Is Artificial Intelligence in Medicine?
Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems capable of analyzing data, learning from it, and making intelligent decisions similar to those made by physicians.
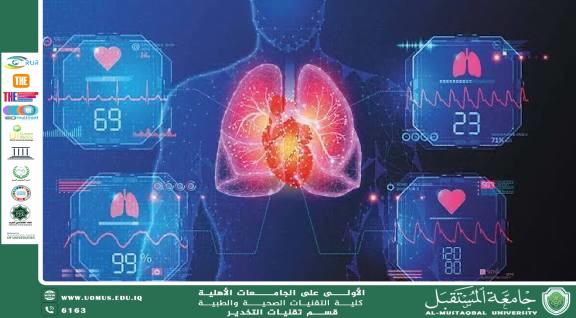
In cardiology, AI is used to analyze ECG readings, medical images, and electronic health records to predict future risks.
From ECG Signals to Diagnostic Intelligence
AI can interpret ECG waveforms with high precision and detect abnormalities that may be overlooked by the human eye.
It can identify early indicators of conditions such as:
• Atrial fibrillation
• Cardiomyopathy
• Life-threatening arrhythmias
Recent studies have shown that algorithms can predict heart attacks weeks before they occur by analyzing subtle patterns in ECG recordings.
Medical Imaging Analysis
Deep learning techniques are used to analyze cardiac CT scans and MRI images.
AI can measure heart wall thickness, blood flow volume, and the condition of the coronary arteries.
This rapid and accurate analysis helps physicians make informed decisions without delay.
Predicting Heart Attacks and Strokes
By integrating data from:
• Electronic medical records
• Blood pressure and cholesterol levels
• ECG results
AI can calculate a patient’s risk of experiencing a future heart attack or stroke, enabling preventive action before it is too late.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology
1. Faster and more accurate diagnosis
2. Reduction of human error
3. Support for physicians in selecting optimal treatment plans
4. Remote patient monitoring through smart devices
5. Early prediction of complications
Challenges and Limitations
• The need for large, high-quality medical datasets to train AI systems
• Ethical considerations surrounding patient data use
• Ensuring AI serves as a tool to assist—not replace—physicians
Conclusion
AI has become a true partner to cardiologists thanks to its ability to analyze medical data with remarkable speed and precision. The near future promises even more advanced medical intelligence capable of saving lives through early prevention and accurate diagnosis.
Zahraa Jawad
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq.