Digital Blood: Advanced Computational Modeling of Blood Properties and Future Clinical Applications Scientific Article by Instructor Mariam Redha)
1. Introduction
The accelerating progress in Computational Modeling and Artificial Intelligence (AI) has led to the emergence of new medical concepts aimed at enhancing diagnostic accuracy and pathological prediction. The concept of Digital Blood is one of these modern trends, relying on the creation of a high-fidelity virtual model that simulates the physical, chemical, and functional behavior of blood within the human circulatory system. Digital Blood represents an extension of the Biological Digital Twin concept, which is used to simulate individual biological processes based on specific patient data.
2. Definition of Digital Blood
Digital Blood is a data-driven virtual system designed to numerically and dynamically represent blood variables, including:
Concentration of blood cells (RBCs, WBCs, Platelets)
Plasma properties
Blood Viscosity
Flow Rates
Coagulation Parameters
This data is utilized within mathematical models and machine learning algorithms to simulate the physiological behavior of blood under both normal and pathological conditions.
3. Scientific Foundations of Digital Blood
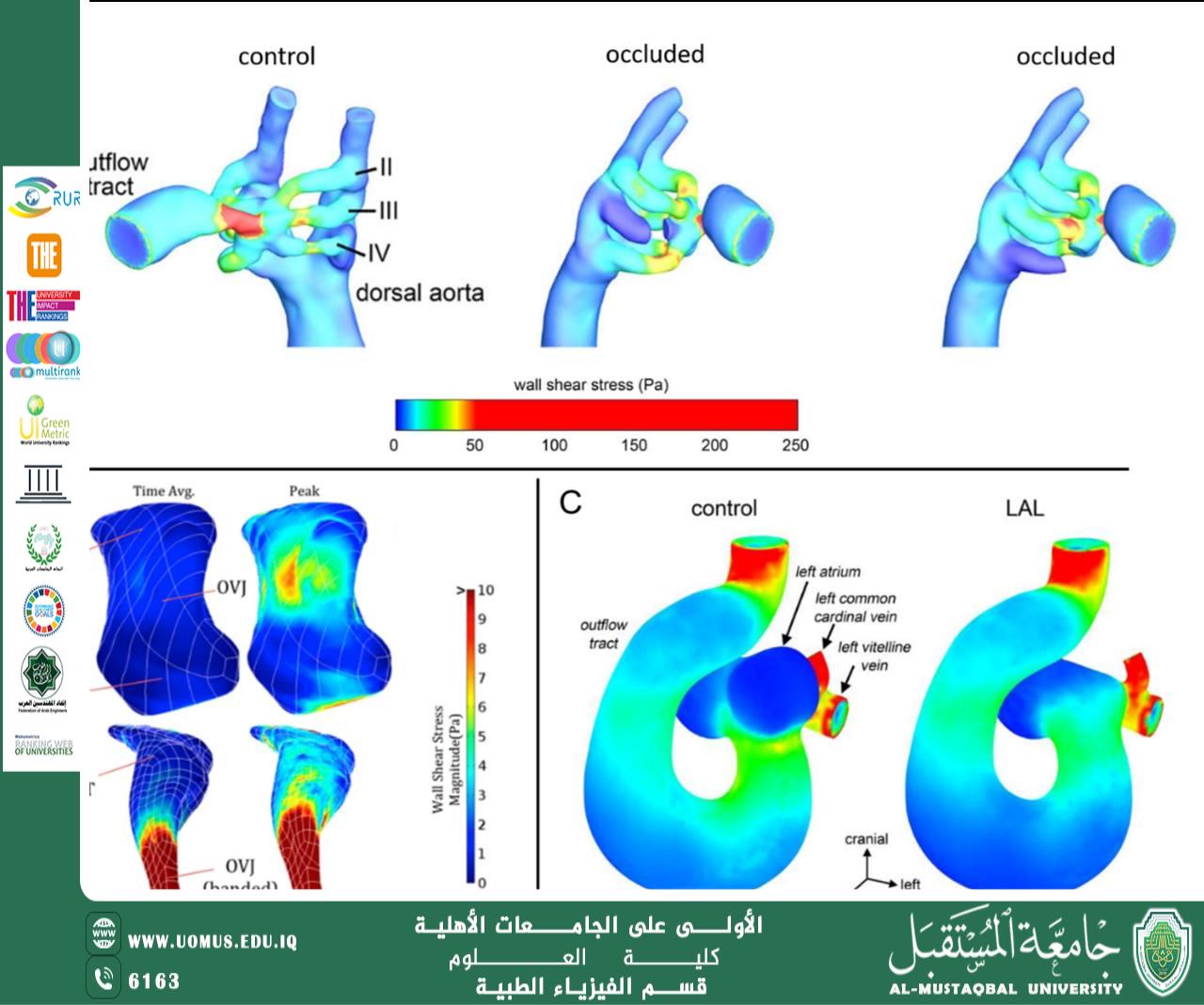
3.1 Mathematical Modeling and Hemodynamics Digital Blood relies on Fluid Dynamics equations, such as: Navier–Stokes equations, and Non-Newtonian Models. This is because blood does not behave like a simple fluid; its viscosity changes depending on flow rate and vessel diameter.
3.2 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Deep Neural Networks and Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Algorithms are employed to discover hidden patterns in blood data and predict the progression of hematological diseases before clinical symptoms appear.
4. Mechanism for Building the Digital Blood Model
The process of building Digital Blood goes through several methodological stages:
Collecting clinical and laboratory data (CBC, PT, APTT, D-dimer, inflammatory markers)
Integrating with imaging data (CT Angiography, MRI Flow Imaging)
Analyzing and digitally processing data
Creating a personalized dynamic computational model
Simulating pathological or therapeutic scenarios
5. Clinical Medical Applications
5.1 Predicting Coagulation Disorders: Digital Blood aids in predicting the risk of clots, assessing the probability of bleeding, and determining optimal drug dosages for anticoagulants.
5.2 Personalized Medicine: It provides a customized model for each patient, rather than relying on general reference values.
5.3 Virtual Drug Testing: The effects of drugs on the blood are tested digitally before administration to the patient, minimizing complications.
6. Scientific and Technical Challenges
Despite the advantages, Digital Blood faces several challenges: the complexity of interaction between blood components, biological variability among individuals, the need for high-quality data, and ethical issues and health information security.
7. Future Vision
Digital Blood is expected to be used in the future in: early preventive medicine, smart emergency rooms, virtual surgery, and space medicine and extreme environments. It may evolve into a routine diagnostic tool complementing traditional laboratory analysis.
8. Conclusion
Digital Blood represents a qualitative leap in understanding the dynamic behavior of blood within the living body, combining biophysics, clinical medicine, and artificial intelligence. With the continued evolution of computational technologies, this concept may become one of the pillars of precision medicine in the near future.
AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq.