Radioactive Materials in Diagnosis: Benefits and Risks - A Scientific Article by Instructor Samaher Saad
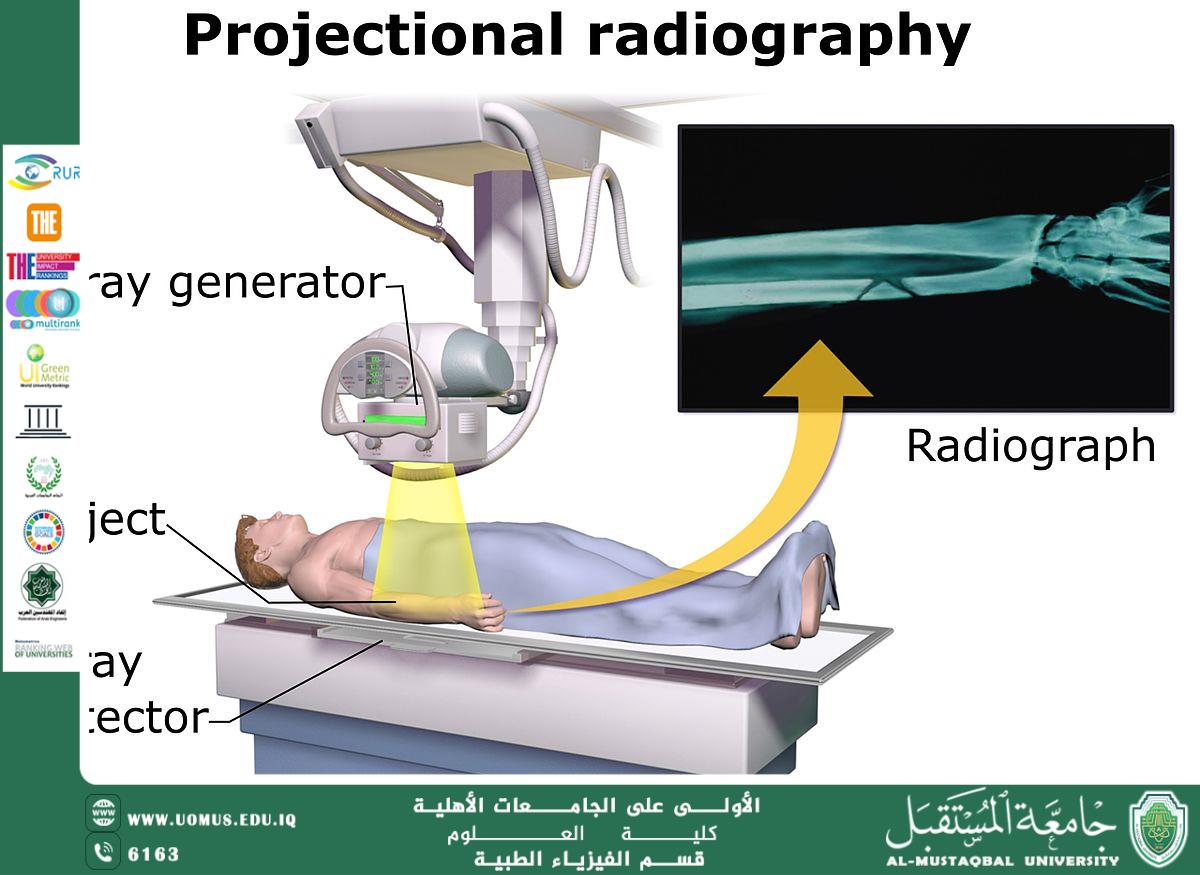
Radiopharmaceuticals play a crucial role in modern medicine, particularly in diagnostic imaging techniques such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Scintigraphy. These substances enable physicians to visualize internal organ function and detect diseases that traditional imaging methods may miss.
Benefits of Radiopharmaceutical Use
Accurate Functional Imaging
Radiopharmaceuticals allow detailed assessment of organ function in the heart, kidneys, thyroid, and brain, offering valuable insights that cannot be obtained through conventional imaging.
Early Cancer Detection
These materials are capable of identifying small tumors and detecting biochemical changes at the earliest stages, which significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Monitoring Treatment Response
Nuclear imaging helps evaluate how well a tumor responds to chemotherapy or radiotherapy, allowing physicians to adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Non-invasive and Patient-Friendly
Most nuclear imaging procedures are minimally invasive and provide patient comfort compared to surgical diagnostic methods.
Risks Associated with Radiopharmaceuticals
Radiation Exposure
Although the doses used are generally low and safe, repeated exposure may pose cumulative risks over time.
Allergic Reactions or Mild Side Effects
Some patients may experience allergies or mild symptoms such as nausea or localized irritation at the injection site.
Not Suitable for Certain Groups
Use in pregnant women is avoided unless absolutely necessary to prevent potential risks to the fetus.
Conclusion
Radiopharmaceuticals are highly effective tools that greatly enhance diagnostic accuracy for many diseases. While their use carries
some risks, proper safety protocols and dose management ensure that the benefits significantly outweigh the potential drawbacks.
"AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq"