A Scientific Article by Lecturer Abbas Hamza Khudhair Titled: The Biochemical Concept of Food and Its Impact on Human Health
The science of food biochemistry is a fundamental pillar for understanding the relationship between food and human health. It studies the chemical elements of nutrients and how they are metabolized within the body through enzymatic, hormonal, and regulated cellular processes. This science contributes to explaining how energy is generated from food, the mechanisms of tissue building and regeneration, and the impact of various dietary patterns on the prevention of chronic diseases.
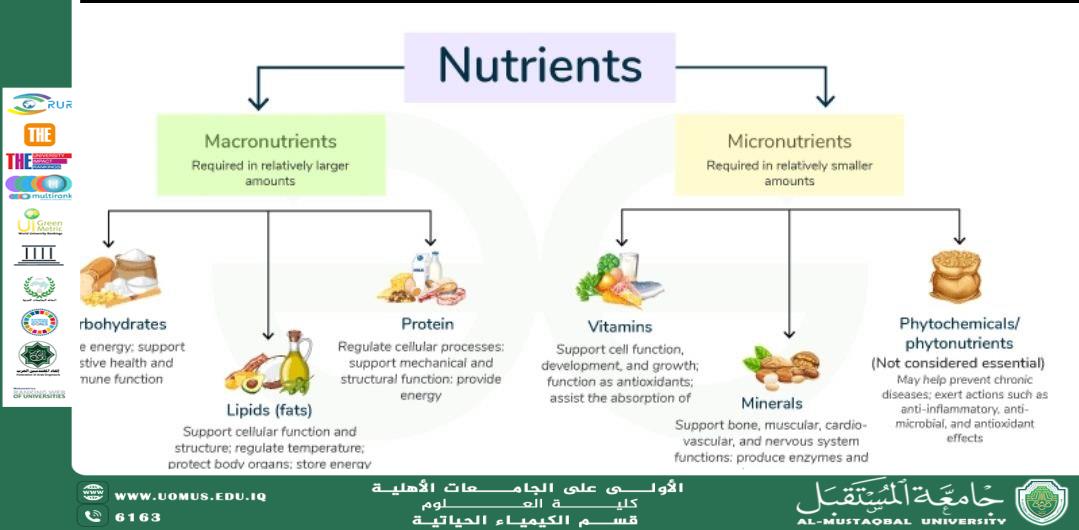
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is defined as a dietary system that provides the necessary requirements of calories, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. For the body to function efficiently, most daily calories should come from:
· Fresh fruits
· Fresh vegetables
· Whole grains
· Legumes
· Nuts
· Lean proteins
The concept of calories refers to the amount of energy contained in food, and this energy is consumed in performing all vital functions. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), produced from the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, is the main source of energy required for muscle movement, brain activity, and the functions of vital organs.
Food Between Health and Disease
Proper nutrition represents the cornerstone of health, while nutritional imbalance leads to serious disorders at the cellular and tissue levels. Excessive intake of sugars, saturated fats, and sodium is associated with increased risks of:
· Type 2 diabetes
· High blood pressure
· Obesity
· Cardiovascular diseases
· Hormonal disorders
· Genetic effects such as DNA damage
Furthermore, the continuous consumption of large amounts of glucose strains the pancreas and leads to insulin resistance. Conversely, the body can utilize ketone bodies produced from fat breakdown as an alternative energy source, a mechanism used in low-carbohydrate diets that has shown notable results in weight control and improved metabolism.
Biochemical Changes During Food Processing
Many foods undergo processing operations such as cooking, canning, fermentation, drying, or the industrial addition of flavors. These processes affect the food's value in various ways:
Benefits of Food Processing:
· Improving digestion through the enzymatic breakdown of proteins.
· Producing bioactive peptides with antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
· Preserving some nutrients like vitamins.
· Extending shelf life and preventing microbial growth.
Drawbacks of Food Processing:
· Loss of some heat-sensitive vitamins.
· Formation of harmful compounds such as heterocyclic aromatic amines during grilling or frying.
· High concentration of sodium and sugars in canned foods.
· Alteration of texture and flavor due to oxidation or chemical decomposition.
Conclusion
Food is a fundamental key to maintaining public health. Understanding the biochemistry of food represents an important step in determining correct dietary choices and recognizing the impact of malnutrition on the emergence of chronic diseases. Adopting a balanced diet based on minimally processed natural foods, while limiting sugars and saturated fats, effectively contributes to promoting health and reducing the risks of non-communicable diseases.
Al-Mustaqbal University is the top-ranked private university in Iraq