A Scientific Article by Lecturer Zahraa Hazim Hamed titled: Photocatalysis for Organic Synthesis Using Solar Energy
Photocatalysis is one of the most advanced trends in modern organic chemistry, providing a reaction pathway that relies on clean, renewable energy sources such as sunlight instead of heat or high-energy chemicals. This field represents a qualitative shift because it enables complex organic reactions to be conducted under mild conditions with high efficiency and less waste, making it a prominent choice for achieving industrial and research sustainability.
The Concept of Photocatalysis
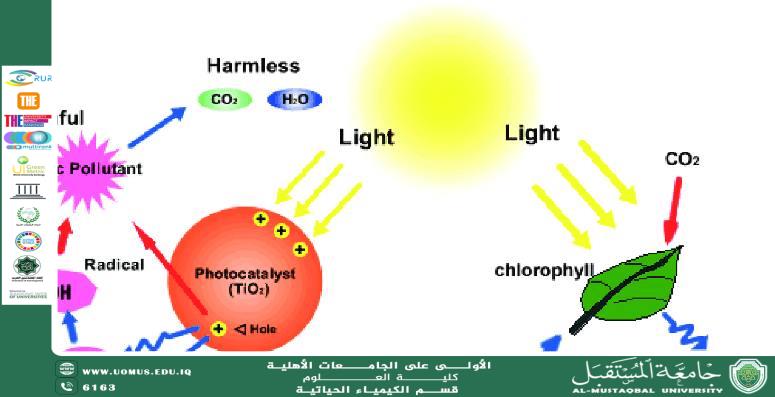
Photocatalysis is the use of light to activate a chemical substance (a photocatalyst) capable of absorbing photons and transitioning to an excited state. This excited state possesses higher energy, allowing it to donate or accept electrons, thereby driving a series of organic reactions that are difficult to achieve through conventional methods.
Photocatalysts include:
1. Organic dyes such as Rose Bengal, Eosin Y, and Rhodamine B
2. Transition-metal photocatalysts such as Ru(II) and Ir(III) complexes
3. Semiconductors such as TiO₂ and ZnO
4. Metal-free photocatalysts, a modern trend
Why Use Sunlight?
Sunlight is a free, renewable, and broader light source than artificial lamps. Relying on it reduces:
· Electrical energy consumption
· Reaction costs
· Toxic gas emissions
· The need for heating or pressure equipment
It also enables reactions under "mild" conditions that preserve the stability of heat-sensitive compounds.
Simplified Mechanism of Photocatalysis
1. The photocatalyst absorbs light.
2. It transitions to an excited state.
3. It gains or loses electrons more readily.
4. It activates the organic substrate via:
· Single Electron Transfer (SET)
· Energy Transfer (EnT)
5. Controlled free radicals are generated, forming new bonds.
6. The photocatalyst returns to its original state to start a new cycle.
This mechanism enables new reaction pathways that were not possible with traditional thermal catalysts.
Key Applications of Photocatalysis in Organic Synthesis
1. C–C Bond Formation
One of its most important uses, enabling the construction of complex organic structures such as:
· Cross-coupling reactions without heavy metals.
· Minisci reactions for adding alkyl or aryl groups.
2. Selective Oxidation and Reduction
Without the need for strong oxidizing agents:
· Oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes.
· Reduction of organic halides to reactive radicals.
3. "Click Photochemistry" Reactions
Fast, clean, and selective reactions used in:
· Medicinal chemistry
· Biochemistry
· Smart material synthesis
4. Photocatalysis in Pharmaceutical Production
Major pharmaceutical companies have begun using it to produce Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) because it is:
· Less costly
· Safer
· Avoids toxic solvents
5. Conversion of CO₂ to Organic Compounds
One of the key areas of sustainability:
· Converting CO₂ to formic acid, methanol, or carboxyl compounds
· Using photocatalysts under sunlight.
6. Synthesis of Organic Polymers
Light-induced polymerization provides:
· Better control over molecular weight
· Smarter and biodegradable polymers
· Purer products
Benefits of Photocatalysis for Sustainability
1. Use of clean energy (sunlight).
2. Reduction of chemical waste.
3. Reduced reliance on heavy metals and toxic catalysts.
4. Lower energy consumption compared to traditional methods.
5. Increased reaction selectivity and reduced by-products.
Recent Examples Published in International Journals
· Use of Ir(ppy)₃ catalyst to convert CO₂ to carboxyl compounds (Nature Chemistry, 2023).
· Development of a metal-free organic catalyst for photocatalysis under direct sunlight (Green Chemistry, 2022).
· Synthesis of C–N bonds using only sunlight and a simple organic catalyst (ACS Catalysis, 2024).
· Use of organic dyes for cross-coupling reactions without metals (Chemical Science, 2023).
Future Challenges
Despite significant progress, challenges remain:
· Difficulty in fully controlling light distribution within reactors.
· The need for cheaper and more stable photocatalysts.
· Challenges in scaling some reactions to industrial levels.
However, research is advancing rapidly, especially with the integration of artificial intelligence in designing new catalysts.
Conclusion
Photocatalysis using solar energy represents a true revolution in organic chemistry. It is not merely a research trend but a new platform for innovating clean, efficient, and environmentally friendly organic synthesis pathways. With significant advancements in photocatalyst manufacturing and solar absorption technologies, this field is poised to become a fundamental pillar of a sustainable chemical industry in the future.
Al-Mustaqbal University is the top-ranked private university in Iraq.