The Impact of Pathogenic Bacteria on Human Health
Pathogenic bacteria are among the leading causes of infectious diseases that directly affect human health. They possess the ability to invade body tissues and cause pathological disorders ranging in severity from mild to severe conditions. This article aims to clarify the concept of pathogenic bacteria, their mechanisms of pathogenicity, the most important diseases they cause, as well as methods of diagnosis, prevention, and treatment.
Introduction
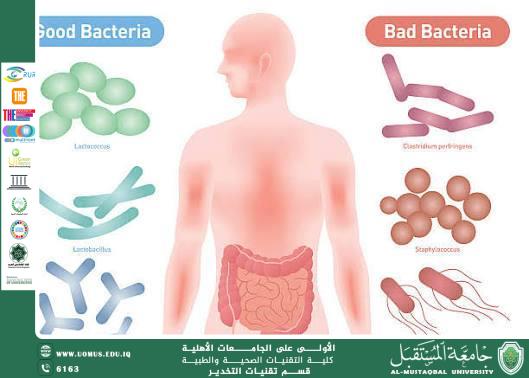
Bacteria inhabit most environments surrounding humans, and many of them are harmless or even beneficial to the body. However, some species are classified as pathogenic bacteria due to their ability to cause disease. Bacterial infections represent a growing global health challenge, particularly with the increasing resistance of bacteria to antibiotics, which necessitates a deeper understanding of their impact on human health.
Concept of Pathogenic Bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria are microscopic living organisms capable of causing disease when they enter and multiply within the human body. Their pathogenic potential varies depending on the type of bacteria, the infectious dose, and the efficiency of the host’s immune system.
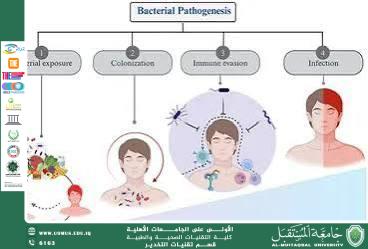
Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenicity
Pathogenic bacteria affect human health through several mechanisms, most notably:
• Production of bacterial toxins that damage cells and tissues
• Invasion of tissues and intracellular or extracellular multiplication
• Induction of excessive inflammatory responses
• Suppression of or evasion from the host immune system
Diseases Caused by Pathogenic Bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria are responsible for numerous diseases, including:
• Respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia and tuberculosis
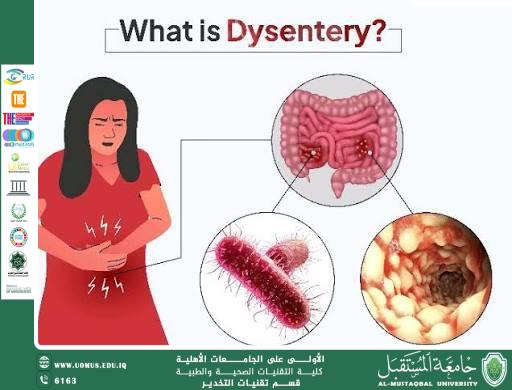
• Gastrointestinal diseases such as typhoid fever and cholera
• Skin and soft tissue infections
• Urinary tract infections
• Sepsis
Impact on Human Health
Bacterial infections lead to various health effects, which may include:
• Fever and general fatigue
• Dysfunction of vital organs
• Chronic complications if left untreated
• Increased mortality rates in severe cases
Bacterial infections also impose a significant economic burden on healthcare systems.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of bacterial infections relies on:
• Clinical examination and medical history
• Laboratory tests such as culture of samples (blood, urine, sputum)
• Molecular diagnostics and rapid detection techniques
• Antibiotic susceptibility testing
Treatment
Treatment of bacterial infections depends on:
• The use of appropriate antibiotics based on the causative organism
• Adherence to prescribed dosages and treatment durations
• Supportive care, such as fluid replacement and fever control
• Monitoring and managing antibiotic resistance
Prevention
Preventive measures against bacterial diseases include:
• Maintaining personal hygiene and regular handwashing
• Vaccination against certain bacterial infections
• Proper food preparation and consumption of clean water
• Rational use of antibiotics
• Enhancing public health awareness
Conclusion
Pathogenic bacteria pose a serious threat to human health, particularly in light of the rising problem of antibiotic resistance. Early diagnosis, effective treatment, and adherence to preventive measures play a crucial role in limiting the spread of bacterial diseases and reducing their health and economic impacts. Health education and continuous scientific research remain essential pillars in addressing this challenge.
Zainab Mohamed Jawad
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq