Obesity and Its Relationship with Anesthesia
Obesity is one of the growing global health challenges and has direct and indirect effects on many medical procedures, particularly anesthesia. This article aims to explain the concept of obesity, highlight its impact on anesthesia, the associated risks, and the most important medical considerations when administering anesthesia to obese patients.
Introduction
The increasing prevalence of obesity has led to a rise in the number of overweight and obese patients undergoing surgical procedures. Anesthesia is one of the medical stages most affected by obesity due to the physiological changes that occur in various body systems, which increase the complexity of anesthetic management.
Concept of Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition resulting from excessive accumulation of body fat. It is commonly diagnosed using the Body Mass Index (BMI), where a person is considered obese if their BMI is equal to or greater than 30 kg/m². Obesity significantly affects the respiratory system, cardiovascular function, and metabolism, all of which are crucial factors in anesthesia.
Concept of Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a medical procedure used to eliminate pain sensation during surgical or diagnostic procedures. It is classified into several types, including:
• General anesthesia
• Local anesthesia
• Regional anesthesia
• Intravenous anesthesia
The choice of anesthesia depends on the patient’s condition and the type of procedure.
Effects of Obesity on Anesthesia
Obesity influences anesthesia in several important ways, including:
1. Respiratory System Complications
Obesity reduces lung volumes and makes ventilation more difficult, increasing the risk of hypoxia during anesthesia.
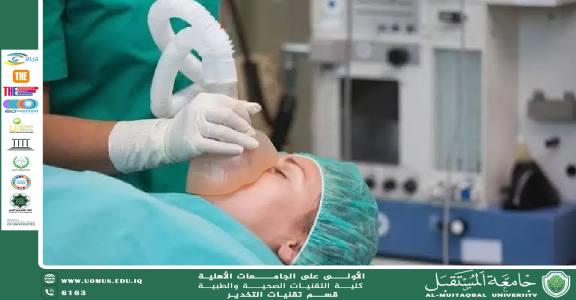
2. Difficulty in Airway Management
Fat accumulation in the neck and pharyngeal tissues may make tracheal intubation more challenging.
3. Cardiovascular Changes
Obesity increases cardiac workload and raises the risk of blood pressure instability during anesthesia.
4. Altered Distribution of Anesthetic Drugs
Excess body fat affects the absorption, distribution, and elimination of anesthetic agents, requiring careful dose adjustment.
Potential Complications
Obese patients have a higher risk of anesthesia-related complications, such as:
• Hypoxia
• Postoperative respiratory depression
• Pulmonary infections
• Delayed recovery from anesthesia
Medical Considerations and Prevention
To minimize anesthesia-related risks in obese patients, the following measures are recommended:
• Thorough preoperative assessment
• Selection of the most appropriate anesthetic technique
• Careful monitoring of respiratory and cardiovascular functions
• Encouraging weight reduction before elective surgeries
Conclusion
Obesity represents a significant risk factor in anesthesia practice, as it increases procedural complexity and the likelihood of complications. Proper planning, careful patient evaluation, and individualized anesthetic management are essential to ensure patient safety and optimal surgical outcomes.
Ameer Bahaa Fahim
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq.