A Scientific Article by Assistant Dr. Karrar Majeed Obaid Title:Biochemistry and Metabolism: The Molecular Basis of Life's Continuity
Biochemistry and Metabolism: The Molecular Basis of Life's Continuity
Biochemistry is a central science that explains biological phenomena at the molecular level, studying the chemical composition of living organisms and the interactions occurring within cells. Among the most important topics in this field is Metabolism, which represents the sum of regulated chemical reactions that ensure a cell’s survival, growth, reproduction, and adaptation to its environment.
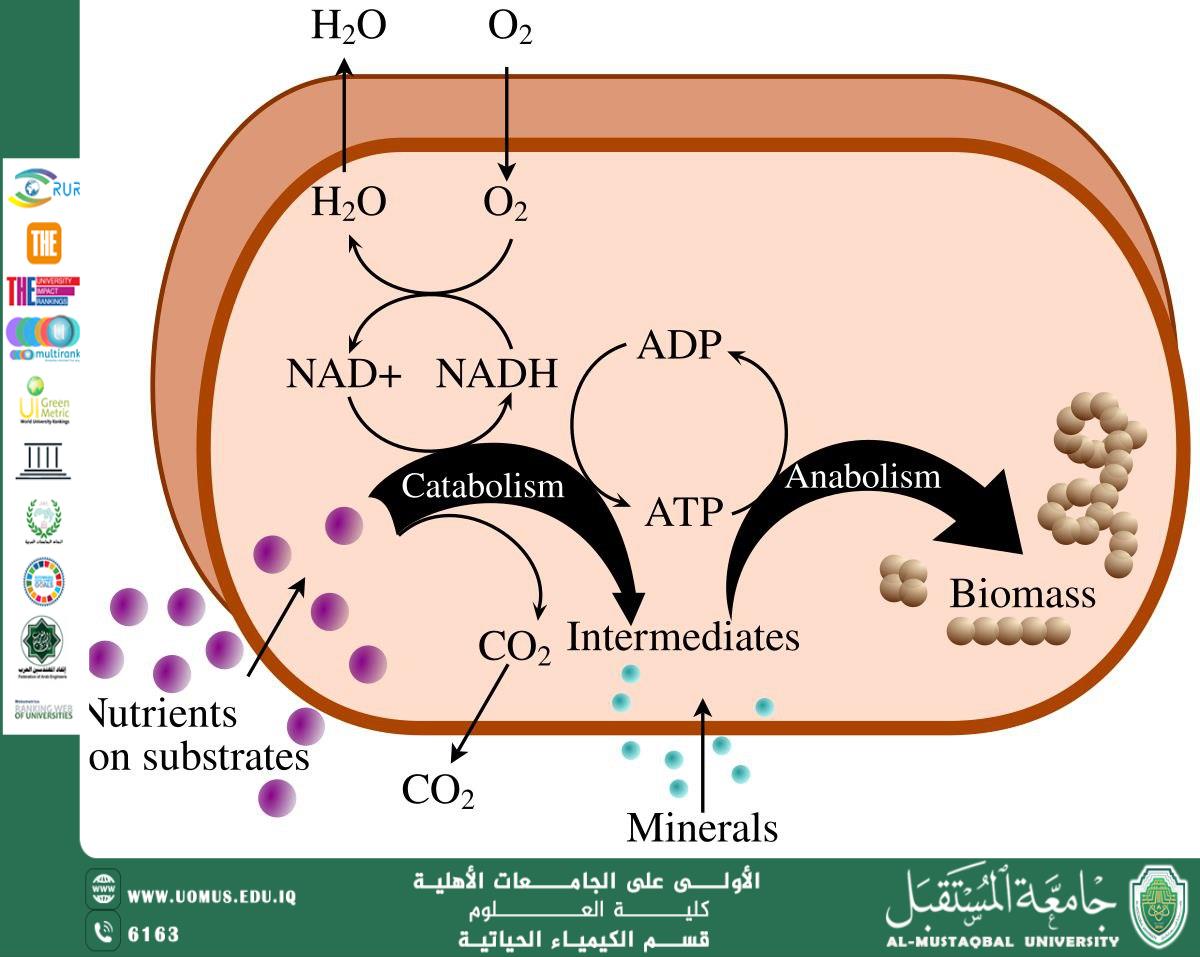
Metabolism relies on a complex network of enzymatic reactions that convert nutrients into energy and essential structural compounds. These reactions are divided into two main pathways: catabolic reactions, which break down complex molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins to produce energy, and anabolic reactions, which use the released energy to build large biomolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids.
Enzymes play a central role in regulating metabolism, acting as highly specialized biological catalysts that lower activation energy and allow reactions to occur under moderate physiological conditions. These enzymes exhibit high precision in substrate binding, ensuring metabolic efficiency and specificity. Metabolic systems are also subject to precise regulatory mechanisms, including allosteric activation and inhibition, hormonal regulation, and changes in gene expression, allowing organisms to respond quickly to environmental changes and energy demands.
Metabolism serves as a fundamental energy source through well-known biological pathways such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain, where the chemical energy stored in food is converted into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's energy currency. The role of metabolism is not limited to energy production; it also includes the removal of toxic waste, maintenance of internal homeostasis, and the provision of intermediate compounds that enter other biological pathways.
Dysregulation of metabolic reactions leads to serious health disorders such as diabetes, inherited metabolic disorders, and neurological diseases. Therefore, the study of biochemistry and metabolism forms the foundation for understanding pathological mechanisms and developing drug treatments and modern medical technologies, including targeted drug design and gene therapy.
In conclusion, biochemistry and metabolism represent the cornerstone of understanding life at the molecular level, revealing the intricate relationships between structure, function, and regulation within the cell. This field remains one of the most evolving and impactful branches of biological sciences, playing a vital role in medicine, pharmacy, biotechnology, and modern applied research.
Al-Mustaqbal University – First among Iraqi Universities