A scientific article by teaching assistant (Ahmed Jalal Naama) entitled "Microscopic Fungi"
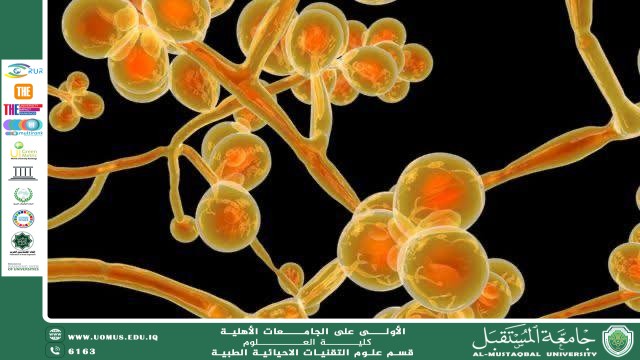
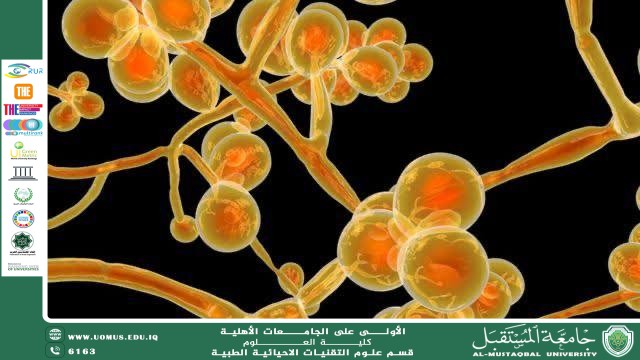
Microscopic fungi are microscopic organisms invisible to the naked eye that live in various environments, such as soil, water, and even inside the bodies of living organisms. Despite their small size, their role in the ecosystem is no less important than that of any other living organism.
What are microscopic fungi?
They are a type of fungus that can only be seen under a microscope. They include species such as yeasts, molds, and some parasitic types. They differ from bacteria in their cellular structure, as their cells contain a true nucleus.
The roles of microscopic fungi in the environment:
1. Decomposition and Recycling:
Microscopic fungi decompose dead organic matter (such as plants and animals), returning nutrients to the soil and aiding plant growth.
2. Symbiotic Relationship with Plants:
Some fungi live in plant roots in a symbiotic relationship called mycorrhizae. The roots help the fungi absorb water and minerals, and the fungi benefit from the sugars produced by the plants. 3. Environmental Purification:
Some types of microscopic fungi can absorb pollutants and break down toxic substances in soil and water, making them useful in bioremediation.
4. Bioproduction:
They are used in the production of antibiotics (such as penicillin), in the manufacture of food and beverages (such as bread and cheese), and in environmental industries.
Examples of Important Microscopic Fungi:
• Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae): Used in bread and beverage production.
• Penicillium: Produces penicillin and is also used in cheese making.
• Rhizopus: Helps in the decomposition of organic matter.
Conclusion: Microscopic fungi are not only part of the ecosystem but are its essential pillars. Without them, organic debris would accumulate, and the soil would lack nutrients. They are invisible environmental soldiers, but vital to the life of the planet.
Al-Mustaqbal University, the leading university in Iraq.