Analysis of Earth Dam Efficiency Using Hydrological Modeling
Assistant Lecturer: Sally Selan Hussein
Introduction
Earth dams are among the most important hydraulic structures used for water storage for irrigation purposes, hydropower generation, and flood protection. With climate change and increasing rainfall intensities, analyzing the efficiency of earth dams has become vital to ensure their safety and sustainability. Hydrological modeling relies on representing water processes within a watershed to evaluate runoff, storage, and the response of dams to rainfall loads and surface runoff.
Concept of Hydrological Modeling for Earth Dams
Hydrological modeling is the process of using mathematical and computer-based models to simulate water movement within a watershed, including surface runoff, infiltration, and water storage in the dam. These models help to:
Estimate peak flows during storm events.
Evaluate the dam’s response to heavy rainfall.
Identify flood and seepage risks.
Improve design and develop operation and maintenance strategies.
Main Components of Hydrological Modeling
Collection of Hydrological and Climatic Data
This includes rainfall rates, temperature, evaporation, and natural discharge data.
Surface Runoff Modeling
Estimating the amount of water reaching the dam reservoir after losses due to infiltration and absorption.
Storage and Discharge Modeling
Determining available storage capacity and maximum safe discharge to ensure dam safety.
Scenario Analysis
Studying dam response under extreme storms, prolonged drought periods, or future climate change conditions.
Modeling Tools and Techniques
HEC-HMS (Hydrologic Modeling System): A widely used model for estimating surface runoff and calculating peak flows.
SWAT (Soil and Water Assessment Tool): Used to assess the impact of land use and agricultural practices on runoff and water storage.
MIKE SHE: An integrated model for simulating both surface and groundwater hydrology.
GIS Tools: Used to analyze watershed topography and flow paths.
Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Earth Dams
Engineering Design Specifications: Dam height and length, slope angle, and type of construction materials.
Hydrological Characteristics of the Watershed: Drainage area, soil type, and permeability rate.
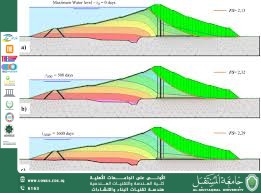
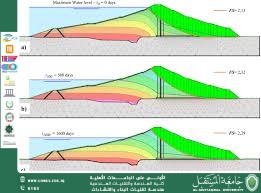
Seepage and Vibrations: Presence of cracks or internal erosion reduces efficiency and increases failure risk.
Operation and Maintenance Conditions: Inspection of channels, gates, and discharge control devices.
Climate Change: Increased rainfall intensity or prolonged droughts affect storage capacity.
Importance of Analyzing Earth Dam Efficiency
Ensuring structural safety and reducing the risk of dam failure.
Improving water management to meet agricultural and industrial demands.
Reducing flood risks in downstream areas.
Supporting long-term operational planning under future climate conditions.
Case Studies and Practical Examples
Chowdhury et al. (2019) showed that using HEC-HMS to analyze earth dams in India improved flood discharge management during the monsoon season and reduced flood risks by 25%.
Li et al. (2020) applied the SWAT model to assess the impact of climate change on river earth dams in China, leading to adjustments in storage and discharge strategies.
Another study demonstrated that combining GIS with hydrological modeling for earth dams in Arab countries helped accurately identify seepage zones and areas prone to failure.
Conclusion
Hydrological modeling represents an effective tool for analyzing the efficiency of earth dams, as it provides accurate estimation of water flows, storage, and dam response to rainfall loads. Integrating mathematical models with field data and GIS systems enhances dam safety, improves water resource management, and reduces flood risks. This highlights the importance of using modern technologies in the design and operation of earth dams to ensure their long-term sustainability.
References (APA 7th Edition)
Chowdhury, R., Saha, S., & Das, S. (2019). Hydrological modeling of earth dams using HEC-HMS for flood mitigation. Water Resources Management, 33(12), 4155–4172.
Li, X., Wang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2020). Assessment of climate change impacts on earth dam performance using SWAT model. Journal of Hydrology, 590, 125–137.
HEC (Hydrologic Engineering Center). (2016). HEC-HMS Hydrologic Modeling System User’s Manual. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.
Maidment, D. R. (Ed.). (2002). Handbook of hydrology. McGraw-Hill.
Sadeghi, S. H., & Azari, H. (2018). GIS-based hydrological modeling for earth dam safety assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(4), 203.