Scientific Difference Between Viruses and Bacteria
First: Definition
Virus
A virus is a non-living microscopic agent outside the host cell. It cannot perform any vital function on its own and depends entirely on the host cell for replication; therefore, it is considered an obligate intracellular parasite.
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled living microorganisms capable of independent growth and reproduction in various environments such as water, soil, and the human body. Some are beneficial, while others are pathogenic.
Second: Size and Visibility
• Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and are measured in nanometers.
• Bacteria can be seen using a light microscope.
• Viruses can only be observed using an electron microscope.
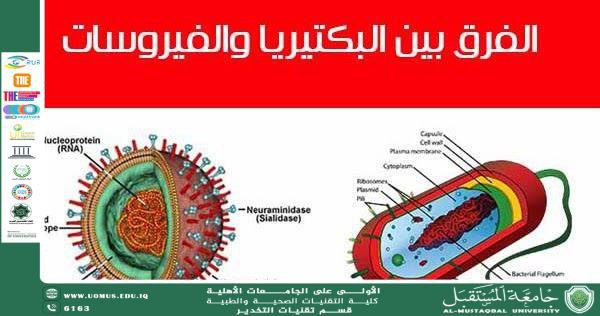
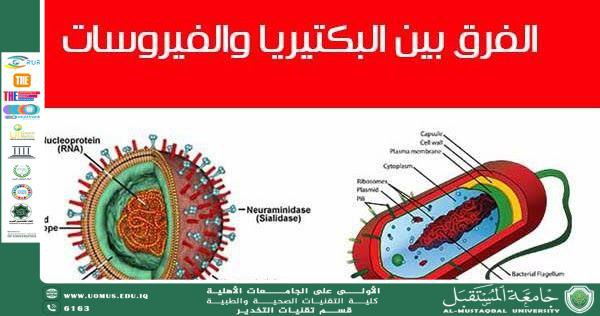
Third: Structure and Composition
Virus:
• Genetic material: DNA or RNA
• Protein coat (capsid)
• Sometimes surrounded by a lipid envelope
Viruses lack:
• Nucleus
• Cytoplasm
• Ribosomes
Bacteria:
A complete cell structure that includes:
• Cell wall
• Cell membrane
• Cytoplasm
• Ribosomes
• Sometimes flagella for movement
• Circular DNA not enclosed within a nuclear membrane
Fourth: Reproduction
Virus:
• Enters the host cell
• Hijacks the cell’s machinery
• Forces it to produce new viral particles
• Viruses exit either by cell lysis or without destroying the cell
Bacteria:
• Reproduce independently through binary fission
• Can double in number every 20 minutes under suitable conditions
• Do not require a permanent host
Fifth: Diseases Caused
Viral diseases:
• Influenza
• COVID-19
• Viral hepatitis
• AIDS
• Measles
Bacterial diseases:
• Bacterial tonsillitis
• Food poisoning
• Urinary tract infections
• Wound infections
• Tuberculosis
Sixth: Treatment
Viruses:
• Antibiotics are completely ineffective
• Treatment depends on:
• Supporting the immune system
• Antiviral drugs (depending on the virus)
• Vaccines for prevention
Bacteria:
• Treated using antibiotics
• The choice of antibiotic depends on:
• The type of bacteria
• Its sensitivity to the drug
Seventh: Prevention
Prevention of viral infections:
• Vaccination
• Hand hygiene
• Wearing masks during outbreaks
• Avoiding direct contact
Prevention of bacterial infections:
• Personal hygiene
• Proper wound disinfection
• Drinking clean water
• Maintaining food hygiene
Hasan Najeh
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq.