The Effect of Calcium Deficiency on Growth
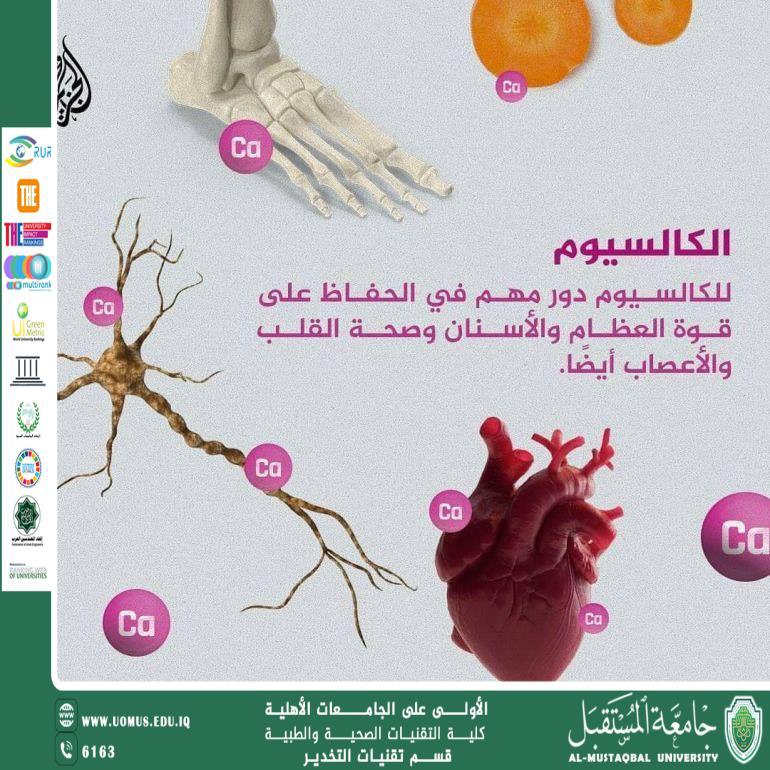
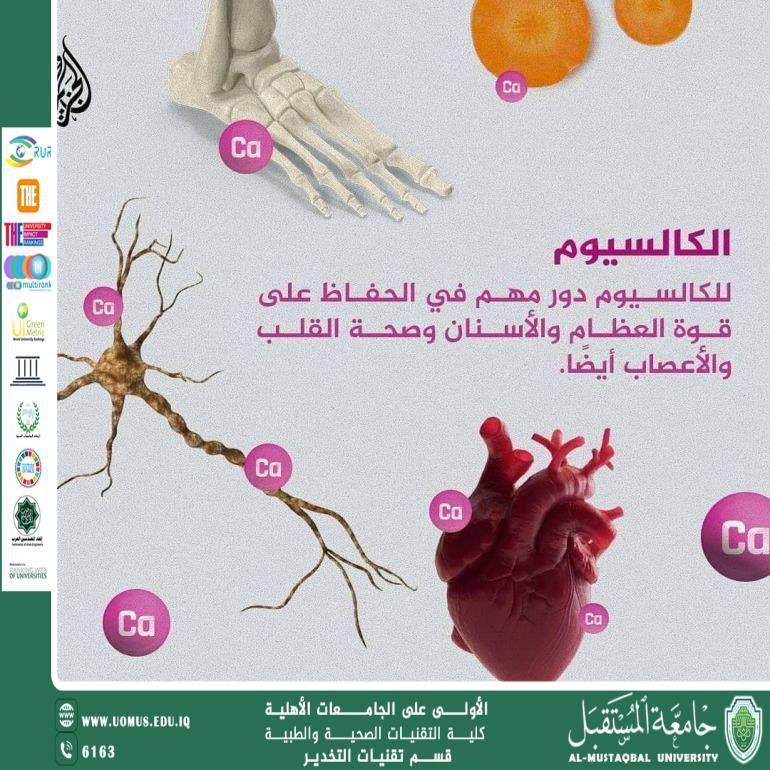
Calcium is one of the most essential minerals in the human body, playing a crucial role in bone and teeth development, muscle function, and nerve signal transmission. Calcium deficiency, particularly during growth stages, leads to health disorders that directly affect physical and functional growth, especially in children and adolescents. This article aims to clarify the effects of calcium deficiency on growth, its causes, health consequences, and methods of prevention and treatment.
Introduction
Calcium is a fundamental mineral that constitutes the main component of the skeletal system. The body requires adequate amounts of calcium during periods of rapid growth, such as childhood and adolescence. Prolonged calcium deficiency may result in delayed growth, weakened bones, and an increased risk of bone-related diseases.
Role of Calcium in Growth
Bone and Teeth Development
Calcium contributes to building bone mass and increasing bone density, ensuring proper growth and strength of bones and teeth.
Muscle Function
Calcium is essential for muscle contraction, and its deficiency may cause muscle cramps and weakness.
Nerve Signal Transmission
It plays an important role in transmitting nerve impulses between nerve and muscle cells.
Hormonal Regulation
Calcium influences the secretion of certain hormones related to growth and metabolic balance.
Causes of Calcium Deficiency
• Inadequate intake of calcium-rich foods such as milk and dairy products
• Vitamin D deficiency, which is essential for calcium absorption
• Gastrointestinal disorders that impair mineral absorption
• Increased requirements during periods of rapid growth
• Disorders of the thyroid or parathyroid glands
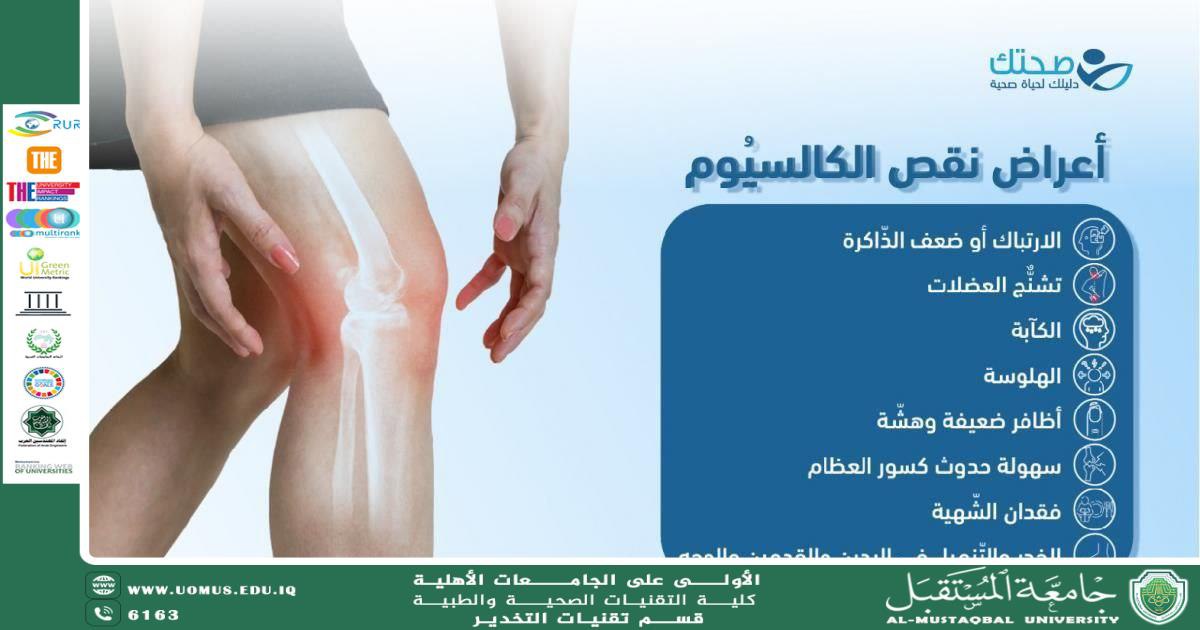
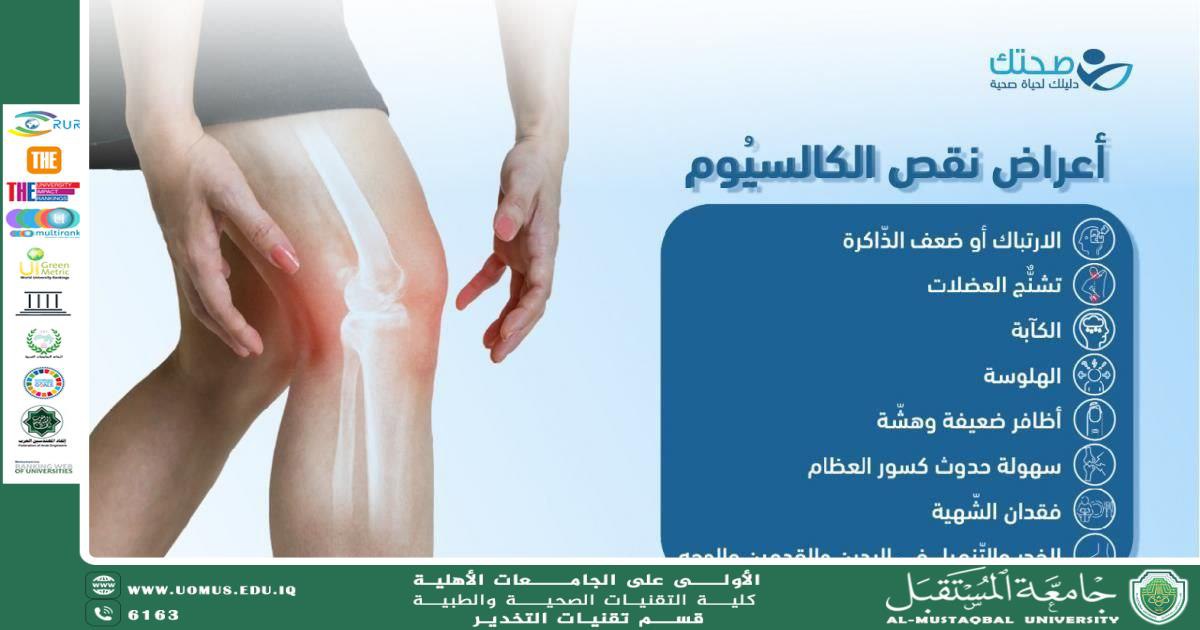
Effects of Calcium Deficiency on Growth
• Delayed linear growth in children
• Reduced bone density and increased fracture risk
• Rickets in children
• Osteoporosis later in life
• Skeletal deformities
• Weak teeth and delayed tooth eruption
Health Consequences
Chronic calcium deficiency leads to long-term health problems, including short stature, reduced physical fitness, and increased susceptibility to bone injuries, negatively affecting overall health and quality of life.
Prevention and Treatment
• Consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium (milk, cheese, leafy green vegetables)
• Adequate exposure to sunlight to stimulate vitamin D production
• Using calcium supplements when necessary under medical supervision
• Nutritional education, especially for children and adolescents
• Regular medical follow-up
Conclusion
Calcium deficiency is a significant health issue that directly affects growth, particularly during early life stages. Early prevention and proper nutrition play a vital role in ensuring healthy growth and reducing future complications.
Ahmed Ibraheem
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq.