A Scientific Article Titled: Autoimmune Liver Diseases: Immunological and Pathophysiological Mechanisms By Instructor: M.M. Abbas Hamza Khudhair
Autoimmune liver diseases are a group of chronic disorders that arise from a dysfunction of the immune system, leading to the attack of liver cells or bile ducts as if they were foreign entities. This abnormal immune response results in chronic inflammation, progressive tissue damage, and may ultimately lead to liver fibrosis or functional failure if not diagnosed and treated early.
Main Types of Autoimmune Liver Diseases
Autoimmune liver diseases include three main entities:
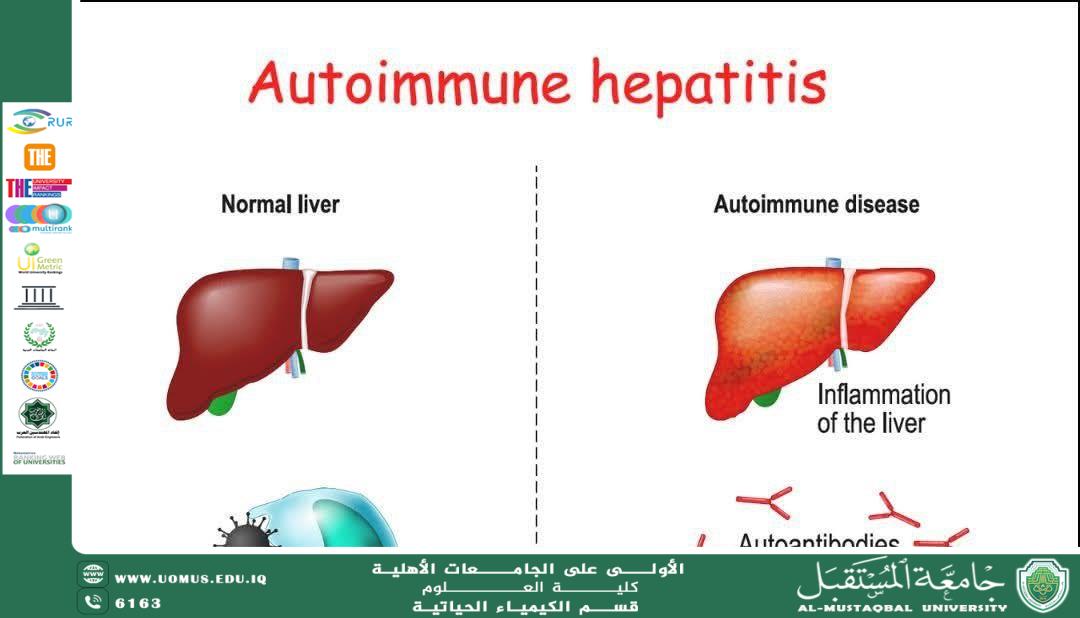
1. Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH)
Characterized by chronic liver inflammation due to T-cell activation and the production of autoantibodies targeting liver cells. It is more common in females and is associated with elevated:
· Liver enzymes (ALT, AST)
· Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
Prominent autoantibodies include:
· Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
· Anti-smooth muscle antibodies (SMA)
· Anti-liver/kidney microsomal type 1 antibodies (anti-LKM-1)
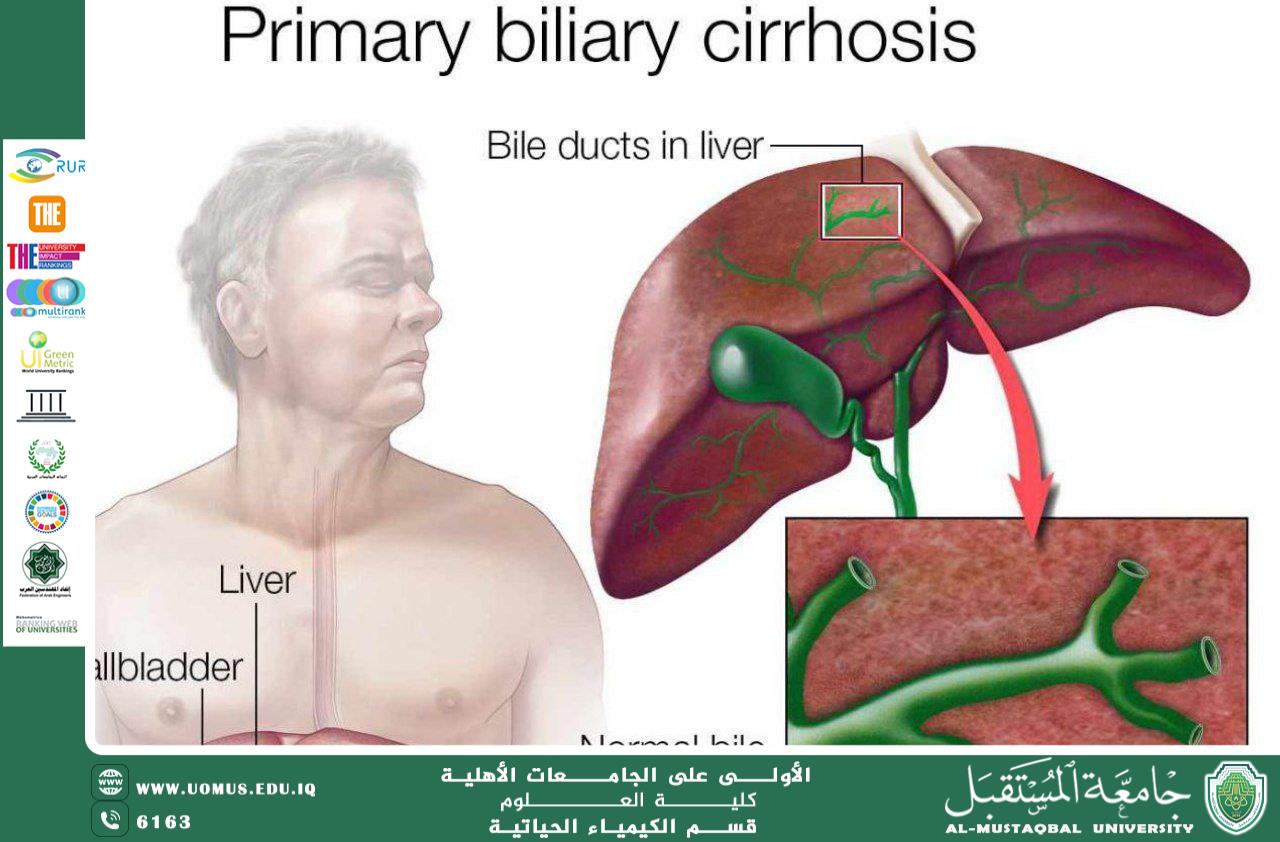
2. Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
A chronic autoimmune disease affecting the small intrahepatic bile ducts, leading to cholestasis and progressive liver damage. It is characterized by:
· Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA)
· Elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
3. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
A chronic inflammatory disease affecting intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts, often associated with inflammatory bowel diseases, particularly ulcerative colitis.
Immunological and Biochemical Mechanisms
These diseases share several pathological pathways, including:
· Loss of immune tolerance
· Activation of T cells and B cells
· Increased inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6)
· Oxidative stress and free radical accumulation
· Activation of hepatic stellate cells and fibrosis formation
These mechanisms disrupt liver structure and impair its vital functions.
Clinical Symptoms
Symptoms range from mild to severe and include:
· Chronic fatigue
· Jaundice
· Pruritus (particularly in PBC)
· Pain in the upper right abdominal quadrant
· Hepatomegaly and splenomegaly
Some cases may be asymptomatic and discovered incidentally through laboratory tests.
Diagnosis and Biomarkers
Diagnosis relies on:
· Liver function tests (ALT, AST, ALP, bilirubin)
· Serological autoantibody tests
· Imaging studies (ultrasound, MRCP)
· Liver biopsy when necessary
Treatment and Management
Treatment aims to suppress the immune response and slow disease progression and includes:
· Corticosteroids
· Immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., azathioprine)
· Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) for PBC
· Regular monitoring to assess fibrosis and complications
In advanced cases, liver transplantation may be the definitive treatment option.
Conclusion
Autoimmune liver diseases represent a significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in clinical practice. Advances in understanding their immunological and pathophysiological mechanisms contribute to early detection, limiting disease progression, and preserving liver function. The role of biochemistry in elucidating the molecular changes driving liver inflammation and fibrosis is also highlighted.
--
University of Al-Mustaqbal Ranks First Among Iraqi Private Universities