A Scientific Article: Applications of Analytical Chemistry in the Medical Field By Instructor: M.M. Haidar Mutlaq Musa
Introduction
Analytical chemistry is a fundamental tool in the medical field,focusing on the accurate measurement of the type and quantity of chemical substances in biological samples. These analyses are used for diagnosing diseases, monitoring health status, and determining appropriate treatments, such as measuring:
· Blood glucose levels
· Proteins
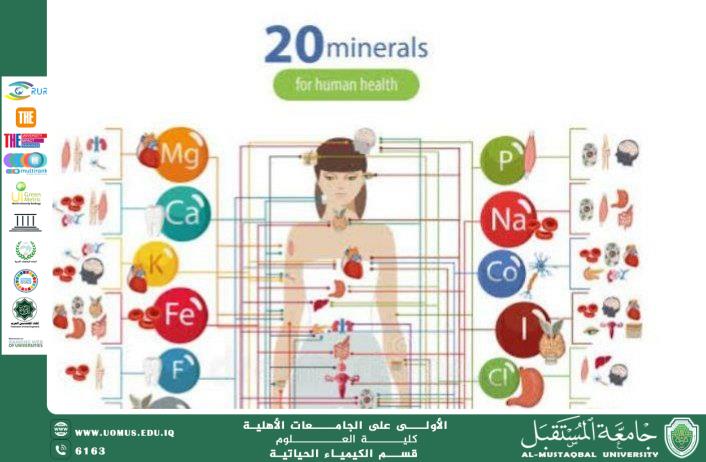
· Minerals
· Enzymes
Principle of Chemical Analysis
Biochemical analyses rely on detecting changes in the chemical or physical properties of a substance when exposed to specific factors such as light or chemical reagents.
Examples:
· Measuring protein absorbance at 280 nm to determine their concentration.
· Reacting reagents with minerals to produce a measurable color using spectroscopic instruments.
Components of Chemical Analysis in the Medical Laboratory
a) Analytical Instruments
· Spectrophotometer (UV-Vis): For measuring absorbance.
· Autoanalyzer: For routine blood and urine analyses.
· Mineral Analysis Instruments: Colorimetric and Atomic Absorption spectrometers.
b) Samples
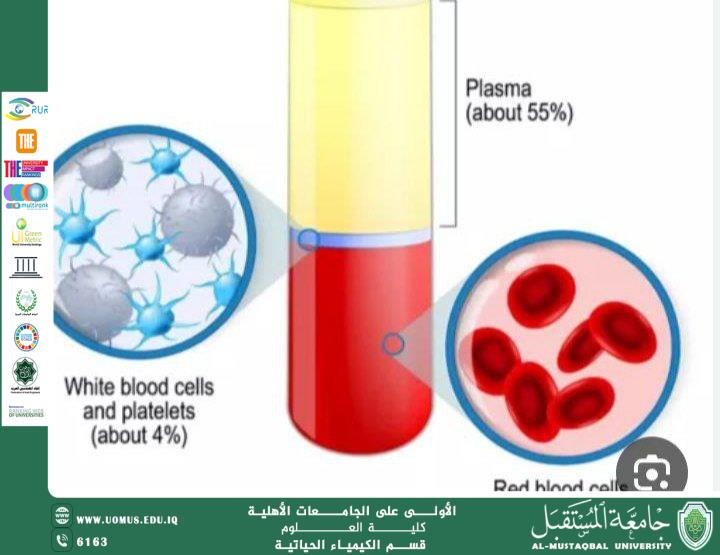
· Blood, urine, or other biological fluids.
· Samples are typically prepared through dilution or the addition of appropriate reagents.
c) Reagents
· Bradford: For serum proteins.
· Xylidyl Blue: For measuring magnesium.
· Specialized reagents for iron and zinc.
Types of Analyses
1. Protein Analysis
· Measuring protein concentrations in blood or serum.
· Common methods: Bradford, Lowry, BCA.
2. Nucleic Acid Analysis (DNA/RNA)
· Determining the concentration and purity of nucleic acids at 260 nm.
3. Enzyme Analysis
· Monitoring enzyme activity through reaction rates and changes in absorbance over time.
4. Analysis of Minerals and Bioactive Factors
· Iron, magnesium, zinc, and copper.
· Colorimetric methods are used for accurate concentration measurements.
Practical Examples
· Zinc (Zn) Measurement: Using the 5-Br-PAPS reagent, measured at 560 nm.
· Magnesium (Mg) Measurement: Using the Xylidyl Blue reagent, measured at 520 nm.
· Protein Analyses: Creating a standard calibration curve with known concentrations to determine the concentration of unknown samples.
Advantages
· High speed and accuracy in analyses.
· Good sensitivity even with small sample volumes.
· Suitable for both routine and research analyses.
Disadvantages
· Results can be affected by sample purity and quality.
· Requires precise instrument calibration.
· Cannot distinguish between substances with similar spectra without advanced methods.
Conclusion
Analytical chemistry plays a pivotal role in the medical field,enabling professionals to diagnose diseases and monitor health status with precision and speed. Analytical instruments such as UV-Vis spectrophotometers and autoanalyzers are key tools for determining bioactive elements, proteins, and enzymes, making them essential in both research and clinical laboratories.
---
University of Al-Mustaqbal Ranks First Among Iraqi Private Universities