Scientific Article by Instructor M.M. Zahra Hazem Hamed, titled: Using Chitin and Chitosan in the Preparation of Innovative Biomaterials
Introduction
With the increasing need for sustainable solutions in various fields, the utilization of renewable natural resources has become a central focus for researchers. Chitin and chitosan are among the most important biopolymers that can be extracted from natural sources such as crustacean shells (shrimp, crab) and some fungi. These two polymers possess unique properties, including biodegradability, absorption and adhesion capabilities, as well as antibacterial properties, making them promising materials for diverse medical, environmental, and industrial applications.
Chitin and Chitosan: Chemical Structure and Preparation
1. Chitin
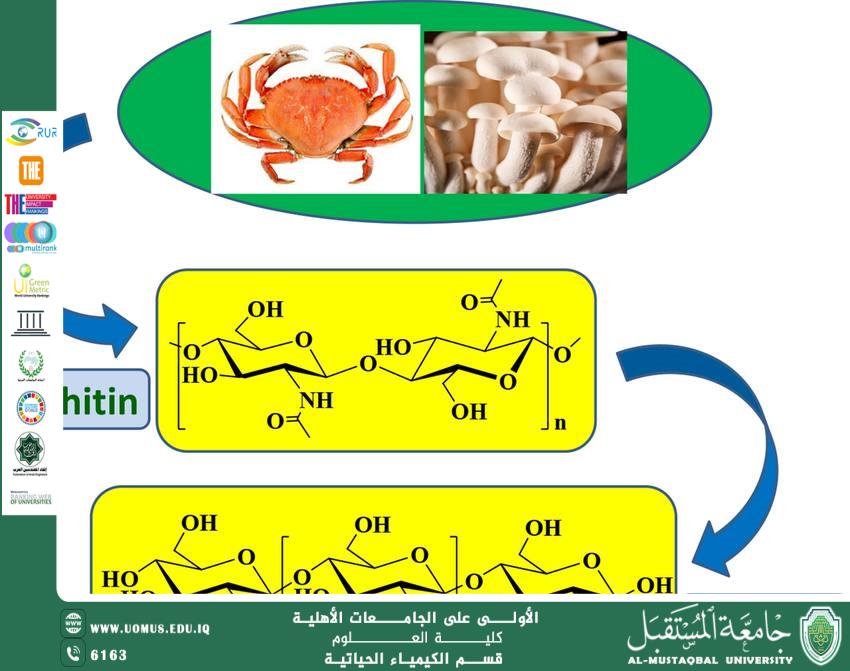
Chitin is the second most abundant natural polymer after cellulose, consisting of N-acetyl glucosamine units linked by glycosidic bonds. It is widely found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans and insects, as well as in the cell walls of certain fungi. It is characterized by high rigidity and biodegradability but is insoluble in water and most organic solvents.
2. Chitosan
Chitosan is prepared by removing acetyl groups from chitin through alkaline treatment (sodium hydroxide), increasing its solubility in weak acidic solutions. Chitosan is known for its unique properties, such as absorption capacity, bioactivity, and low toxicity, making it suitable for a wide range of biological applications.
Innovative Biomedical Applications of Chitin and Chitosan
1. Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
Chitosan is widely used in the medical field due to its antibacterial and biodegradable properties:
· Preparation of biological dressings: Chitosan promotes wound healing and prevents infection, as it is used in the manufacturing of membranes and medical dressings for treating wounds and burns.
· Drug delivery: Drug delivery systems based on chitosan are being developed to protect sensitive drugs and enhance their efficacy. It is used to produce drug-loaded nanoparticles for improved absorption and targeted cell delivery.
· Tissue engineering: Chitosan is used to create three-dimensional biological scaffolds that support cell growth and the regeneration of damaged tissues.
2. Water Treatment and Environmental Applications
Chitosan has a high absorption capacity, making it useful in water treatment technologies:
· Removal of heavy metals: Chitosan absorbs toxic ions such as lead, cadmium, and mercury from polluted water, making it an environmentally friendly material for industrial wastewater treatment.
· Purification of organic dyes: Chitosan is used to remove industrial dyes from textile factory wastewater, contributing to reduced environmental pollution.
3. Food and Biopackaging Applications
· Natural preservatives: Chitosan is used as a natural preservative in the food industry due to its antibacterial and antifungal properties, helping extend the shelf life of food products.
· Biopackaging films: Environmentally friendly packaging films based on chitosan are being developed to replace traditional plastics, helping reduce plastic waste.
4. Agricultural Applications
· Stimulating plant growth: Chitosan enhances natural plant immunity and increases resistance to diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
· Preparation of smart fertilizers: Agricultural materials based on chitosan are being developed for the slow and sustainable release of nutrients, improving fertilizer efficiency and protecting the environment.
Conclusion
Chitin and chitosan are promising natural biopolymers that contribute to sustainability across various fields. From medicine and pharmaceuticals to water treatment and agriculture, these two polymers offer innovative and environmentally friendly solutions that can replace harmful traditional materials. With ongoing research and development, these materials are expected to play a key role in the future of biotechnological industries.
---
University of Al-Mustaqbal Ranks First Among Iraqi Private Universities